17.3 SCALING VERSUS POWER CONSUMPTION
Scaling is an important factor that affects power consumption. As technology is scaled, power supply voltage should also be scaled to maintain the same power density as shown in Fig. 17.2. It is clear from the figure that if the supply voltage is scaled by 1/k the power consumption is scaled by a factor 1/k2 although the power density remains constant. It is also clear that if supply voltage is not scaled then the power density increases in a cubic manner.
The reduction in supply voltage is also accompanied by an increase in circuit delay Td in accordance with the lst-order equation [6];
![]()
Fig. 17.3 shows a plot of delay with supply voltage for a threshold voltage of 0.7 V. It is clear from the figure that the delay for Vdd = 1.5 V is about 10 times the delay for Vdd = 5 V.
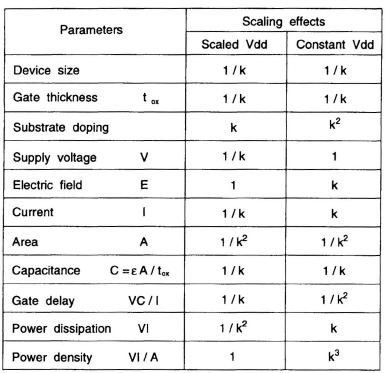
Fig. 17.2 Effect of scaling on power consumption.
One approach to reducing the supply voltage without sacrificing speed is to modify the Vt of the devices. However, the limits on how much Vt can be reduced is set by adequate noise margins and subthreshold leakage currents. Typically, the optimum Vt is determined based on the gates of the CMOS devices and the control of the leakage currents. It is found that for 80−100 mV reduction in Vt (at room temperature), the subthreshold ...
Get VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems: Design and Implementation now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

