5.4 DECODER-ONLY BASED PLC TECHNIQUES
Speech signals are known to contain significant short-duration redundant information, and human perception can allow certain artificially created short-duration voice signals in place of lost signals. In the decoder, the PLC algorithm produces these signals by making use of the history of the samples. During lost packets, the PLC algorithm extrapolates the missing voice samples, and on receiving a good packet, it interpolates for smooth continuity. The PLC algorithm stores a history of the previous speech samples to the extent of 50 ms to regenerated missing speech samples. Figure 5.3 shows a packet drop in the middle of good packets.
In Fig. 5.3, packets 17 and 18 are lost together because of packet drop or they are delayed beyond current acceptable conditions. These packets are assumed to be of 10-ms duration. The PLC algorithm creates synthetic extrapolated speech based on packets 12–16. Interpolation-based algorithms use good packets like 19 and beyond to arrive at the interpolated speech. Interpolation delays the packets and introduces more delay than extrapolation. Different receiver-based recovery techniques are classified as illustrated in Fig. 5.1. A pictorial example of the techniques is given in Fig. 5.3. From the figure, the following observations can be made.
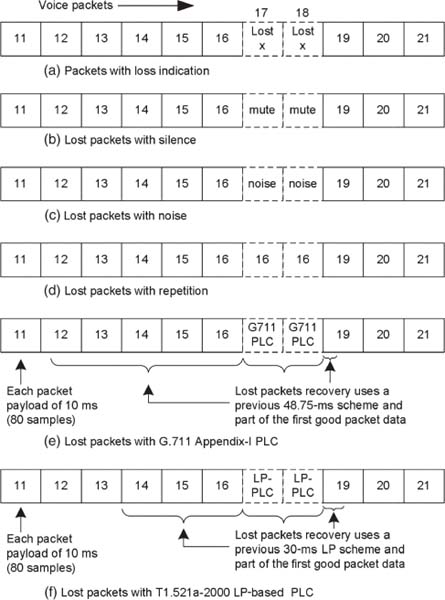
Figure 5.3. Decoder-based PLC techniques. (a) Packet flow with two packets ...
Get VoIP Voice and Fax Signal Processing now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

