CHAPTER 11
Specific Models
11.1. STOCHASTIC RATES AND DEFAULT
The combination of the static default model described in Chapter 10 and a stochastic rates model like the Hull-White discussed in Chapter 8 is now straightforward. The spot rate r—that is, instantaneous riskless borrow rate—follows a risk-neutral process consistent with arbitrage-free bond pricing in the HJM framework,
dr = (v2(t) − k(r − f(t)) + f′ (t)) dt − σ dz(t)
for an initial (riskless) forward curve f(t); model specifications σ and k (both constants; the spot rate standard deviation and the bond volatility/mean reversion decay rate respectively) and
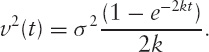
According to this model, a riskless zero-coupon bond, ZT(r, t), has value
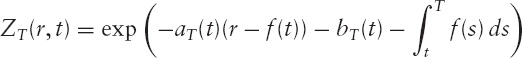
where
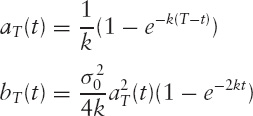
and it satisfies the pricing equation implied by the short rate process,
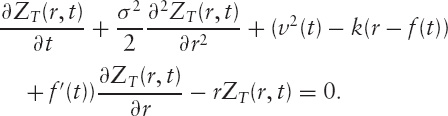
Now a simple model combining rates and default might be: the spot rate continues the above process independently of default; default is a jump-probability event (i.e., it is not stochastic and a known constant probability curve for default exists) and the probability of default is not correlated to the riskless rates ...
Get The Mathematics of Derivatives: Tools for Designing Numerical Algorithms now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

