11.4 Semantic Networks Following the MultiNet Formalism
The relation extraction described here is based on semantic networks that follow the MultiNet formalism, which was devised by Hermann Helbig [21]. The semantic networks are automatically created by applying a deep syntactico-semantic parser to a text corpus. A semantic network is a graph where the nodes represent concepts and the arcs represent relations between the concepts (or functions involving concepts). Lexicalized concepts correspond to word readings. A lexicalized concept name is given by the lemma and two numbers specifying the homograph and the sememe. For details on the numbering scheme see Ref. [21].
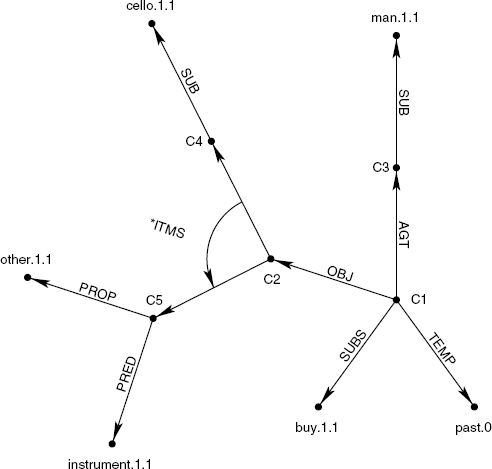
An example of such a semantic network is given in Figure 11.1. The central sentence node, which represents the meaning of the entire sentence, is labeled c1. The actor or agens (MultiNet relation: agt) of the situation expressed by the sentence is a certain man, which is an instance (MultiNet relation sub) of the generic concept man.1.1. The *itms function combines several concepts in a conjunction, in this case the concepts representing the two constituents: cello and other instruments.
Figure 11.1 Example semantic network for the sentence Der Mann kaufte ein Cello und andere Instrumente / “The man bought a cello and other instruments.” For better readability, English concept names are used in the figure.
Sample relations ...
Get Statistical and Machine Learning Approaches for Network Analysis now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

