2.2 Representation of Networks
Networks are represented as sets of nodes and edges drawn between the nodes; thus, networks are essentially similar to “graphs” in mathematics. Examples of networks representing real-world systems are listed in Table 2.1.
Table 2.1 Examples of Nodes and Edges in Networks Based on Ref. [4]
| Network | Nodes | Edges |
| Internet | Computer or router | Cable or wireless data connection |
| World Wide Web | Web page | Hyperlink |
| Citation relationship | Article, patent, or legal case | Citation |
| Power grid | Generating station or substation | Transmission line |
| Friendship network | Person | Friendship |
| Metabolism | Metabolite | Metabolic reaction |
| Food web | Species | Predation |
There are several types of networks (graphs); the major types are shown in Figure 2.1.
Figure 2.1 Examples of small networks: a simple network (a), a directed network (b), and a weighted network (c) in which the numbers along the edges correspond to the weights. The integers in circles correspond to the labels for nodes.
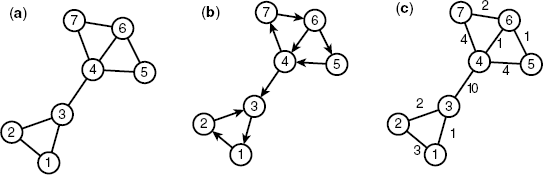
In the simplest case, networks are represented as shown in Figure 2.1a. The relationship (or interaction) between two given nodes is represented in a network by drawing edges between the nodes. In this case, multiedges, which refer to multiple edges between the same pair of nodes, and self-edges, in which the source is identical to the target, are neglected for simplicity. However, the above-mentioned ...
Get Statistical and Machine Learning Approaches for Network Analysis now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

