7.9 High-Bandwidth Modulators
In this section, we shall present some recent developments in which both small size and high bandwidth have been reported.
7.9.1 Ring Resonator
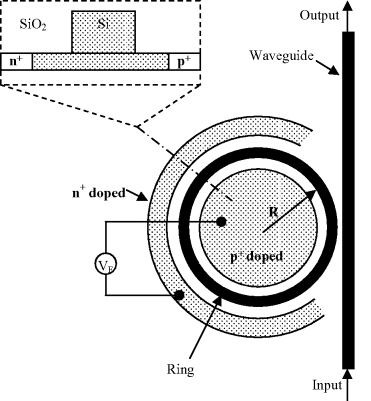
A compact modulator using a ring resonator has been reported by Xu et al. 29, the bandwidth of which exceeds 12.1 Gb/s, and by Li et al. 30. The basic structure by Xu et al. is shown in Figure 7.8. The inset gives a schematic cross-section of a ridge waveguide with an integrated lateral p–i–n diode. The applied bias injects carriers into the ring, thereby changing its RI. The high Q of the resonator ![]() 4 × 104; the authors could achieve modulation depth of >15 dB and a speed of 12.1 Gb/s. The diameter of the ring was 12 µm.
4 × 104; the authors could achieve modulation depth of >15 dB and a speed of 12.1 Gb/s. The diameter of the ring was 12 µm.
Figure 7.8 Structure of a ring resonator. The inset shows the pin structure to inject carriers. Reproduced from [29]. Copyright (2007) Optical Society of America.
7.9.2 MZ Modulators at 10 Gb/s and Above
As mentioned earlier, the speed of the modulator is determined by how fast the carriers decay after the modulating voltage is turned off. A reverse bias applied to the pin diode grown around the waveguide sweeps the carriers out of the waveguide very quickly, so as not to affect the speed, which is ultimately governed by the RC time constant.
The technique has been applied by Intel workers to ...
Get Silicon Photonics: Fundamentals and Devices now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

