7.5 Probability Distributions
The probabilities of events fall within one of several probability distributions. Using the Craps example again and using a bar chart to display the distribution of events and their corresponding probabilities, we see a very discrete distribution (Fig. 7.1).
Figure 7.1 Discrete distribution.
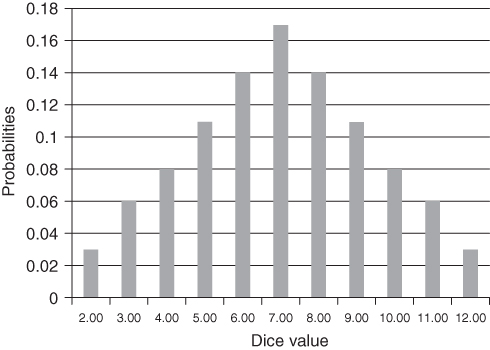
A discrete distribution is just as it sounds, the values of the variable are discrete. For instance, there is no such thing as a 7.5 on a pair of dice. It is a value of 7 or 8. Same as with the probabilities of heads or tails on a coin, they are discrete values.
Another example of a discrete distribution would be the probabilities associated with a certain type of car being in a wreck. These are discrete numbers associated with a certain type of vehicle. Common types of discrete variables would be the
- number of times an electrical switch is thrown before failure;
- number of cycles of an airplane before failure of a component;
- number of demands on a fire suppression system before failure;
- number of demands on a backup diesel generator before failure.
However, in some cases, depending on the range of values, a discrete type distribution can appear continuous.
The alternative to discrete distributions is continuous distributions. The number of hours drivers operate a vehicle between accidents can range from some fraction of one to thousands of hours. The values ...
Get Risk Assessment: Tools, Techniques, and Their Applications now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

