2.8 DAC/ADC Quantization Noise and Clipping
“Digital to analog” and “analog to digital” converters are the two mixed signal blocks in the transmission and reception paths, respectively, bridging the RF AFE and the DBB. Figure 2.39 presents the transfer function of a 3-bit ADC. We can easily imagine the complementary transfer function for a DAC. For communication systems it is preferable to have a large number of bits in order to reduce the quantization noise and a high clipping level for minimizing the signal saturation. These two impairments will degrade the overall transceiver performance and have to be taken into account in the early stage of system design.
Figure 2.39 Transfer function of a 3-bit ADC
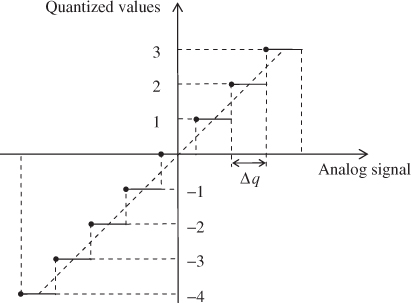
2.8.1 SNR Limitation due to the Quantization Noise and Clipping Level
Quantization noise is generated by the rounding operation performed by the converter when selecting a quantized word from a continuous analog signal. If we define Aclip as the converter clipping level and nbits the converter resolution in number of bits, the quantization resolution Δq is given by
if the number ![]() . The quantization resolution is in same units as the analog signal.
. The quantization resolution is in same units as the analog signal.
The average quantization noise ...
Get RF Analog Impairments Modeling for Communication Systems Simulation: Application to OFDM-based Transceivers now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

