Boxing and Unboxing Types
Boxing and unboxing are the processes that enable value types (e.g., integers) to be treated as reference types (objects). The value is "boxed" inside an Object, and subsequently, "unboxed" back to a value type.
Boxing Is Implicit
Boxing is an implicit conversion of a value type to the type Object. Boxing a value allocates an instance of Object and copies the value into the new object instance, as shown in Figure 18-5.
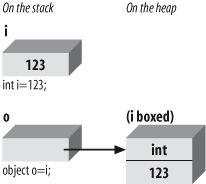
Figure 18-5. Boxing reference types
Boxing is implicit when you provide a value type where a reference is expected and the value is implicitly boxed. You can, of course, explicitly cast the value type to a reference type:
Dim myIntegerValue as Integer = 5 Dim myObject as Object = myIntegerValue ' explicitly cast to object myObject.ToString()
This is not necessary, however, since the compiler will box the value for you:
Dim myIntegerValue as Integer = 5 myIntegerValue.ToString() ' boxed for you
Unboxing Must Be Explicit
To return the boxed object back to a value type, you must explicitly unbox it if Option Strict is On (as it should be). You will typically unbox by using the DirectCast() function or the CType() function.
Figure 18-6 illustrates unboxing.
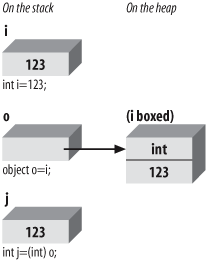
Figure 18-6. Unboxing
Get Programming Visual Basic 2005 now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

