Chapter 4. PRINTING REPORTS
CHAPTER OBJECTIVES
Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to
Distinguish between detail reports, exception reports, and summary reports.
Explain how a printer spacing chart is used to design a printed report.
Describe what should appear in report headings.
Explain the difference between report headings and column headings.
Demonstrate how record types for printer files are defined in the WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
Explain the term "editing" and demonstrate how different editing features are used.
Explain how spacing is controlled when printing a report.
Explain page overflow and how it is used to print headings on a report.
TYPES OF REPORTS
Printed reports fall into three major categories:
Detail reports.
Exception reports.
Summary or group reports.
DETAIL REPORTS
Detail reports are those reports that include one or more lines of output for each input record read. Thus, a detail report is produced when data from each input record are required. For example, printing employee checks from a master payroll file would be an example of a detail report. Another example of a detail report is a list of each employee and their hours worked, as shown in Figure 4.1.
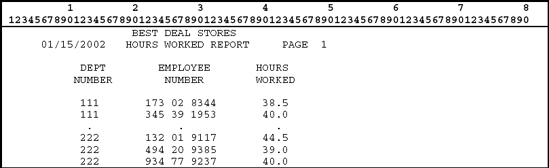
Figure 4.1. Example of a detail report.
EXCEPTION REPORTS
Sometimes users ask for detail reports when, in fact, other types of output would be more useful. For example suppose an insurance agent requests a listing ...
Get PROGRAMMING IN COBOL/400: 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

