Detailed Message Flows
The illustrations in the following sections show ideal message flows. Currently, the translator is not necessarily working this way.
Registration
Figure 15-2 shows the registration process.
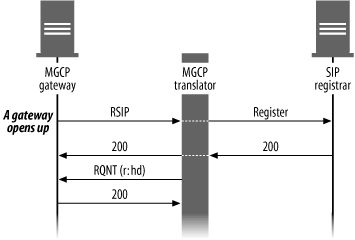
Figure 15-2. Registering MGCP endpoints via RSIP
During registration, the gateway starts up and sends an RSIP message to the translator.
Tip
RSIP coincidentally contains the letters SIP. This has no correspondence to the fact that the translator is talking to a SIP-based system. RSIP simply stands for restart in progress.
The SIP side of the translator, acting as a SIP endpoint, registers with VOCAL, as discussed in Chapter 8, and returns a 200 OK message to the gateway. The translator also sends a Request Notify (RQNT) message requesting notification when the gateway goes off-hook. As long as the gateway is registered, the translator, acting as a gateway controller, maintains stateful control over the gateway. The gateway returns a 200 message in reply to this request.
Basic Call
Figure 15-3 shows the call flow for a basic call from the calling party’s point of view.
Off-hook
The gateway notifies the CA that it has gone off-hook (o: hd), and the CA responds that it received the message (200) and requests notification for when a matching
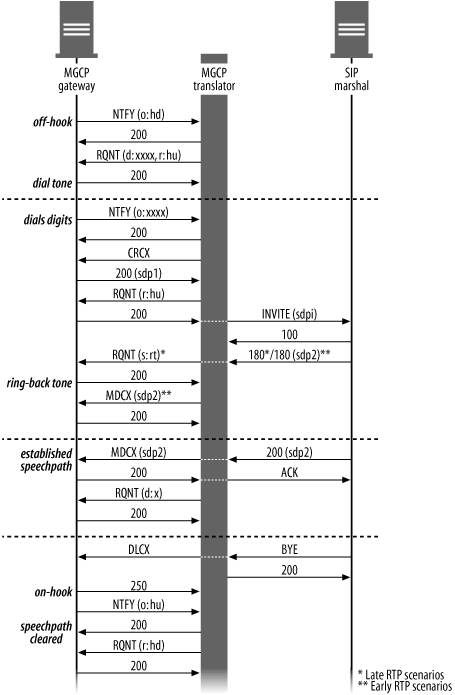
Figure 15-3. Basic call from the caller point ...
Get Practical VoIP Using VOCAL now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

