25.2 TRACKING SCENARIOS IN WSNs
In general, two categories, target tracking and event boundary determination are mainly concerned for tracking tasks in WSNs. Target tracking aims at identifying the location of the target at any moment. For example, in Figure 25.1, a lion existing in the national park is viewed as a mobile target. The sensors in the vicinity of the route of the lion are able to detect the lion, so that these sensors are regarded as the active sensors to be responsible for lion tracking.
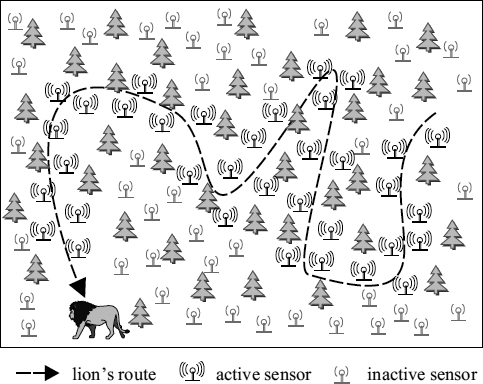
Figure 25.1 Illustration of target (lion) tracking.
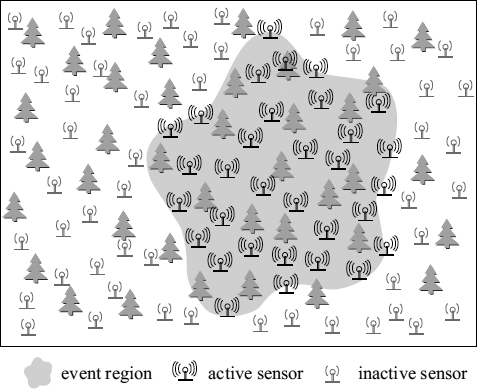
Figure 25.2 Illustration of event (fire) determination.
Alternatively, the main goal of event determination is to enable the sensors within the event region to track the event. Figure 25.2 illustrates a national park, in which the scene of a fire is represented by the shaded region. Here, the fire can be viewed as an event. Obviously, once detecting the fire, the sensors within the event region should become active sensors for fire tracking.
Get Mobile Intelligence now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

