Three Ways We Can Do Filtering
Consider how a Unix machine, or in fact any machine capable of IP routing, processes IP datagrams. The basic steps, shown in Figure 9.2 are:
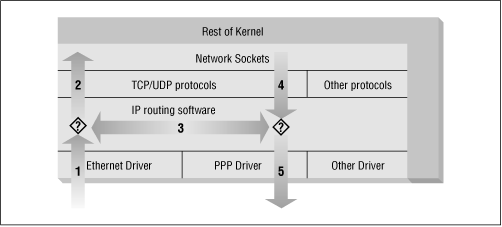
Figure 9-2. The stages of IP datagram processing
The IP datagram is received. (1)
The incoming IP datagram is examined to determine if it is destined for a process on this machine.
If the datagram is for this machine, it is processed locally. (2)
If it is not destined for this machine, a search is made of the routing table for an appropriate route and the datagram is forwarded to the appropriate interface or dropped if no route can be found. (3)
Datagrams from local processes are sent to the routing software for forwarding to the appropriate interface. (4)
The outgoing IP datagram is examined to determine if there is a valid route for it to take, if not, it is dropped.
The IP datagram is transmitted. (5)
In our diagram, the flow 1→3→5 represents our machine routing data between a host on our Ethernet network to a host reachable via our PPP link. The flows 1→2 and 4→5 represent the data input and output flows of a network program running on our local host. The flow 4→3→2 would represent data flow via a loopback connection. Naturally data flows both into and out of network devices. The question marks on the diagram represent the points where the IP layer makes routing decisions.
The Linux kernel IP firewall is capable of ...
Get Linux Network Administrator's Guide, Second Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

