Drawing and Filling Shapes
Example 12-6
lists a GraphicsExample
implementation that shows how various Shape objects can be defined, drawn, and
filled. The example produces the output shown in Figure 12-4. Although the Java 2D
API allows basic shapes to be drawn and filled using the methods
demonstrated in Example
12-1, this example uses a different approach. It defines each
shape as a Shape object, using
various classes, mostly from java.awt.geom.
Each Shape is drawn
using the draw( ) method of the
Graphics2D class and filled using
the fill( ) method. Note that each
Shape object is defined with one
corner at (or near) the origin, rather than at the location where it
is displayed on the screen. This creates position-independent objects
that can easily be reused. To draw the shapes at particular locations,
the example uses the translate( )
method of Graphics2D to move the
origin of the coordinate system. Finally, the call to setStroke( ) specifies that drawing be done
with a two-pixel-wide line, while the call to setRenderingHint( ) requests that drawing be
done using antialiasing.
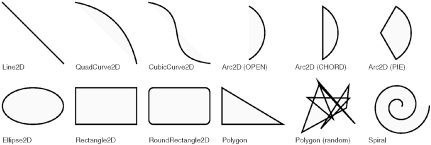
Figure 12-4. Drawing and filling shapes with the Java 2D API
Example 12-6. Shapes.java
package je3.graphics; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.geom.*; import java.awt.font.*; import java.awt.image.*; /** A demonstration of Java2D shapes */ public class Shapes implements GraphicsExample { static final ...Get Java Examples in a Nutshell, 3rd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

