Notes on IP Options
There can be many options in a single IP datagram, up to the amount of free space available in the IP header. Since an IP header can only be 60 bytes long at most—and since 20 bytes are already in use by the default fields—only 40 bytes are available for options.
Options are identified using three separate fields as shown in Figure 2.23: Option-Type, Option-Length, and Option-Data. The Option-Type field is used to indicate the specific option in use, while the Option-Length field is used to indicate the size of the option (including all of the fields and Option-Data combined). Since each option has unique characteristics (including the amount of data provided in the option-data field), the Option-Length field is used to inform the IP software of where the Option-Data field ends (and thus where the next Option-Type field begins).
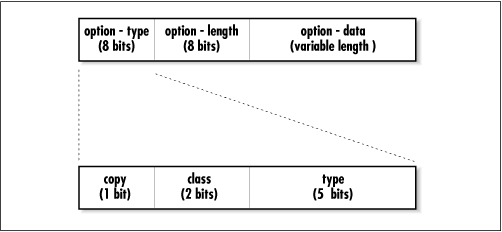
The Option-Type field is eight bits long and contains three separate flags that indicate the specific option being used: copy, class, and type.
The first bit from the Option-Type field indicates whether or not an option should be copied to the headers of any IP fragments that may be generated. Some options—particularly those that dictate routing paths—need to be copied to each of the fragments’ headers. Other options do not need to be copied to every fragments’ headers, and will only be copied ...
Get Internet Core Protocols: The Definitive Guide now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

