Name
Transfer-Encoding: encoding_type
Synopsis
The Transfer-Encoding header specifies that the
message is encoded. This is not the same as content-encoding (an
entity-body header, discussed later), since transfer-encodings are a
property of the message, not of the entity-body. For example:
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
In the HTTP 1.1 specification, chunked is the only
encoding method supported.
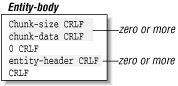
The chunked transfer-encoding encodes the message
as a series of chunks followed by entity-headers, as shown in Figure 1.6. The chunks and entity-headers are in a
client’s request entity-body or server response entity-body.
Each chunk contains a chunk size specified in base 16, followed by
CRLF. After that, the chunk body, whose length is specified in the
chunk size, is presented, followed by a CRLF. Consecutive chunks are
specified one after another, with the last chunk having a length of
zero followed by CRLF. Entity-headers follow the chunks, terminated
by a CRLF on a line by itself.
 |
Get HTTP Pocket Reference now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

