Appendix C. phpMyAdmin
There are a number of third-party user interfaces to MySQL that make it easier to access and alter the data stored in your MySQL databases. The most popular of these, by far, is phpMyAdmin , a web-based application written in PHP.
To install phpMyAdmin, you need first make sure
you have a web server running PHP 4.x or later that either includes
or has been configured to include MySQL database support. You will
also need network connectivity to a MySQL server, even if that MySQL
server happens to be on the same host as the web server running
phpMyAdmin. The
phpMyAdmin
package can be downloaded from
http://www.phpmyadmin.net/, or
your Unix/Linux distribution might make a binary package available
through its native package management system. Debian Linux users, for
example, can simply run apt-get
install
phpmyadmin.
The Basics
To use phpMyAdmin to access your database, you need a username and password that are valid for connections from your web server. Your web server might be on the same machine as your MySQL server, in which case, obviously, the user only needs to be able to access the server from localhost.
Once you have logged in using a valid user account, you will see something that looks like Figure C-1.
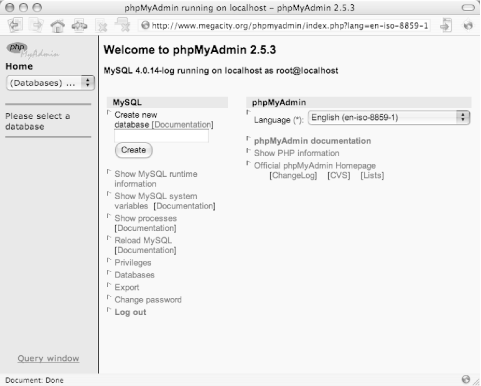 |
As you can see in Figure C-2, there are some links to basic server information. Via the Status link, phpMyAdmin provides a ...
Get High Performance MySQL now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

