RS-422
Unlike RS-232C, which is referenced to local ground, RS-422 uses the difference between two lines, known as a twisted pair or a differential pair , to represent the logic level. Thus, RS-422 is a balanced transmission, or in other words, it is not referenced to local ground. Any noise or interference will affect both wires of the twisted pair, but the difference between them will be less affected. This is known as common-mode rejection . RS-422 can therefore carry data over longer distances and at higher rates with greater noise immunity than RS-232C. RS-422 can support data transmission over cable lengths of up to 1200 meters (approximately 4000 feet).
Figure 10-9 shows a basic RS-422 link, where a driver (D) is connected to a receiver (R) via a twisted pair. The resistor, Rt, at the receiving end of the twisted pair is a termination resistor. It acts to remove signal reflections that may occur during transmission over long distances and is required. Rt is nominally 100-120Ω.
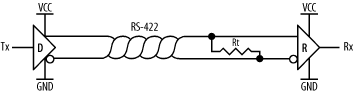
Figure 10-9. RS-422
The voltage difference between an RS-422 twisted pair is between ±4V and ±12V between the transmission lines (Figure 10-10). RS-422 is, to a degree, compatible with RS-232C. By connecting the negative side of the twisted pair to ground, RS-422 effectively becomes an unbalanced transmission. It may then be mated with RS-232C. Since the voltage levels of RS-422 fall within the acceptable ...
Get Designing Embedded Hardware now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

