CATEGORICAL DATA
The chi-square statistic that is so often employed in the analysis of contingency tables,
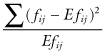
does not have the chi-square distribution. That distribution represents an asymptotic approximation of the statistic that is valid only with very large samples. To obtain exact tests of independence in a 2 × 2 table, use Fisher’s Exact Test.
Consider Table 6.4, in which we have recorded the results of a comparison of two drugs. It seems obvious that Drug B offers significant advantages over Drug A. Or does it? A chi-square analysis by parametric means in which the value of the chi-squared statistic is compared with a table of the chi-square distribution yields an erroneous p-value of 3%. But Fisher’s Exact Test yields a one-sided p-value of only 7%. The evidence of advantage is inconclusive and further experimentation is warranted.
TABLE 6.4. Comparison of two drugs
| Drug A | Drug B | |
| Response | 5 | 9 |
| No Response | 5 | 1 |
As in Fisher [1935], we determine the proportion of tables with the same marginals that are as or more extreme than our original table.
The problem lies in defining what is meant by “extreme.” The errors lie in failing to report how we arrived at our definition.
For example, in obtaining a two-tailed test for independence in a 2 × 2 contingency table, we can treat each table strictly in accordance with its probability under the multinomial distribution (Fisher’s method) ...
Get Common Errors in Statistics (and How to Avoid Them), 4th Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

