4.2 LP-BASED SOURCE-SYSTEM MODELING FOR SPEECH
Speech is produced by the interaction of the vocal tract with the vocal chords. The LP analysis/synthesis framework (Figures 4.1 and 4.2) has been successful for speech coding because it fits well the source-system paradigm for speech [Makh75] [Mark76]. In particular, the slowly time-varying spectral characteristics of the upper vocal tract (system) are modeled by an all-pole filter, while the prediction residual captures the voiced, unvoiced, or mixed excitation signal. The LP analysis filter, A(z), in Figure 4.1 is given by
![]()
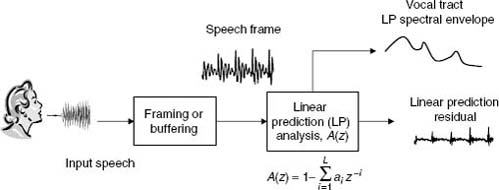
Figure 4.1. Parameter estimation using linear prediction.
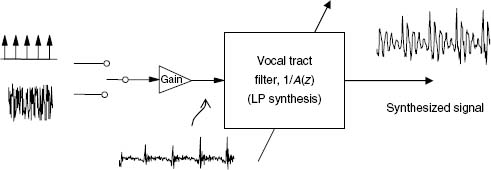
Figure 4.2. Engineering model for speech synthesis.
where L is the order of the linear predictor. Figure 4.2 depicts a simple speech synthesis model where a time-varying digital filter is excited by quasi-periodic waveforms when speech is voiced (e.g., as in steady vowels) and random wave-forms for unvoiced speech (e.g., as in consonants). The inverse filter, 1/A(z), shown in Figure 4.2, is an all-pole LP synthesis filter
![]()
where G represents the gain. Note that ...
Get Audio Signal Processing and Coding now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

