Algorithm-Based Ranking Systems: Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking
Understanding how crawling, indexing, and ranking works is helpful to SEO practitioners, as it helps them determine what actions to take to meet their goals. This section primarily covers the way Google, Yahoo!, and Microsoft operate, and does not necessarily apply to other search engines that are popular, such as Baidu (China) and Naver (Korea).
The search engines have several major goals and functions. These include:
Crawling and indexing the billions of documents (pages and files) accessible on the Web
Responding to user queries by providing lists of relevant pages
In this section, we’ll walk through the basics of these functions from a nontechnical perspective. This section will start by discussing how search engines find and discover content.
Crawling and Indexing
Imagine the World Wide Web as a network of stops in a big city subway system. Each stop is its own unique document (usually a web page, but sometimes a PDF, JPEG, or other file). The search engines need a way to “crawl” the entire city and find all the stops along the way, so they use the best path available: the links between web pages, an example of which is shown in Figure 2-11.
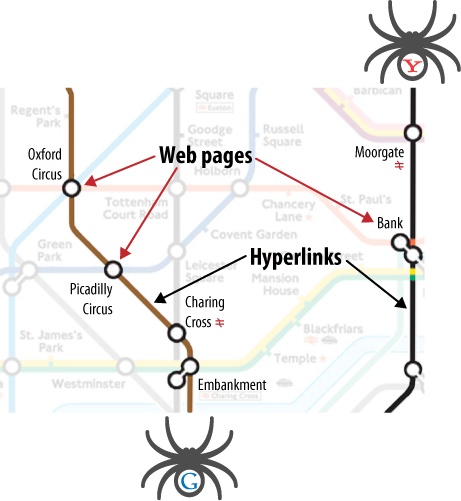
Figure 2-11. London’s Tube used as an analogy for web crawling
In our representation in Figure 2-11, stops such as Embankment, Piccadilly Circus, and Moorgate serve as pages, while ...
Get The Art of SEO now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

