Name
R=
Synopsis
The
R= delivery agent equate specifies a rule set to
be used for processing all envelope- and header-recipient addresses
for a specific delivery agent. Mail messages are always addressed to
at least one recipient, but there can be more. The addresses of the
recipients are given in the envelope and are usually repeated in the
mail message’s header.[16] The envelope
address is given to sendmail in one of three
ways: as a command-line argument; as a RCPT TO: command; or as
To:, Cc:, and
Bcc: headers (if the -t
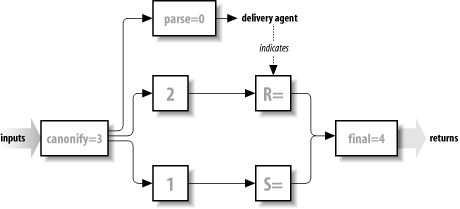
command-line switch is given).[17] Figure 20-1 shows how the
R= rule set fits into the flow of addresses
through rule sets.
 |
There are two forms for the R= delivery agent
equate. One is the standard form, and the other is an enhanced
alternative beginning with V8 sendmail:
R=ruleset ← legal for all R=eset/hset ← legal beginning with V8
In the first case, ruleset specifies the
rule set to use in rewriting both headers and the envelope. If that
value is zero or if the entire R= delivery agent
equate is missing, no rule set is called.
In the second case, two rule sets can be specified.[18] One rule set is
specific to the envelope, and the other is specific to headers. The
envelope-specific rule set is the one to the left of the slash; the
header-specific rule set is to the right
(R=eset/hset). If both values are missing, ...
Get Sendmail, 3rd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

