Retaining Values at Transaction Commit
We have seen how reading data outside a transaction results in
caching nontransactional instances. Another way for nontransactional
instances to exist in the cache is to execute a transaction and then
retain the field values at commit time. You can specify this behavior by
setting the RetainValues property to true. This
is shown in Figure
14-2.
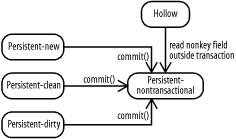
Figure 14-2. RetainValues at transaction commit
With RetainValues set to
true, persistent transactional
instances transition to persistent-nontransactional at commit. But with
RetainValues set to false, fields of persistent transactional
instances are cleared at transaction commit, and the instances
transition to hollow.
The result is that your application can use the cached instances between transactions, and the instances used in the transaction retain their last-committed values. Instances not used in transactions remain nontransactional.
Since the RetainValues flag
only affects the behavior of transaction commit( ), your application can change it at
any time, using setRetainValues( ) in
Transaction. Regardless of how many
times the value changes, the value currently in effect at commit is
used.
Get Java Data Objects now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

