Name
Table → Convert → Text to Table
Synopsis
The Text to Table command converts virtually any text to a table. Anything from a tabbed list to a series of paragraphs can be turned into a table by determining the number of columns and rows, applying an AutoFormat (if desired), and selecting the delimiter (a character or code that tells Word where to break the text to place it in individual cells).
The Convert Text to Table dialog (Figure 10-20) works pretty much like the Insert Table dialog used to create a new table. First, choose the number of columns and rows for the new table. Next, specify how the columns should be sized. These options are covered earlier in the chapter. Finally, choose the type of character that delimits, or separates, the items in the text that should be placed in individual cells. For example, select commas and a new cell is created for each comma in the original text. Use the Other option to enter a custom delimiter.
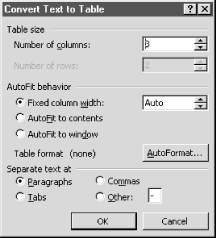
Figure 10-20. Converting text to a table
The most common text-to-table conversion involves tabbed text. Converting the tabbed list in Figure 10-21 creates a three-column, four-row table.
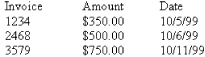
Figure 10-21. Tabbed lists are easily converted to tables
Show Hidden Formatting Before Converting Text to a Table
Before using either of the Convert submenu’s commands, ...
Get Word 2000 in a Nutshell now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

