Horizontal Rules
The simplest element you can add to a web page is a horizontal rule,
plopped into place with the <hr> tag. In
most browsers, horizontal rules display by default as an
“embossed” shaded rule that extends across the full width
of the browser window (or available text space). Horizontal rules are
used as simple dividers, breaking an otherwise long scroll into
manageable chunks.
Since it is a block-level element, a horizontal rule will always
create a line break above and below. If you want additional space
between the rule and the surrounding elements, insert
<p> tags above and/or below the
<hr>, as shown in Figure 9.1.
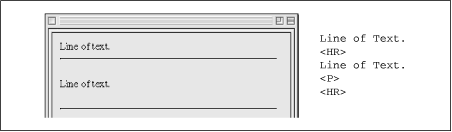
Figure 9-1. Inserting a <p> tag adds vertical space above or below a horizontal rule
There are a few attributes for the <hr> tag
that allow authors to “design” rules more to their
liking. They allow you to change the width, height, alignment of the
rule. You can also opt to turn off the 3-D shaded effect using the
noshade attribute.
Specifying Thickness
The size attribute controls the thickness or
weight of the rule. Size is specified in number of pixels. See Figure 9.2
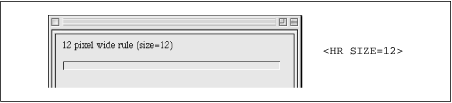
Figure 9-2. A 12-pixel rule
Specifying the Rule Length
Somewhat counterintuitively, the length of the rule is controlled by
the width attribute (corresponding to the width of the page, I suppose). ...
Get Web Design in a Nutshell now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

