53D Cross-Point Array Memory
5.1 Overview of Cross-Point Array Memory
Cross-point array architecture has a potential for achieving a fast, random access, nonvolatile memory with the highest density and smallest cell size possible. The recent exploration of nonvolatile resistance memory elements that can be placed at the cross-point of word-lines and bit-lines has helped realize this potential. If this memory element is no larger than the pitch of these lines (2F), the cell is 2F × 2F (4F2) in area. If this cross-point array can be stacked with another cross-point array, then the density of memory elements is doubled. If stacked with 10 arrays, then the density of memory elements is multiplied by 10. An example of a cross-point array stack with memory elements is shown in Figure 5.1. The cross-point array architecture is considered a potential future competitor for large, high-density NAND flash memory applications. An optimum cross-point switch memory would consist of minimum-size memory elements at the cross-points of a stacked array of perpendicular wires.
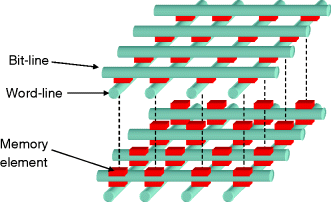
Figure 5.1 Typical cross-point array stack with memory elements at the cross-points.
Theoretically, this stack can be very high and the wire grid very small, allowing the maximum density of data storage to be obtained. An individual cell would need to be externally selectable without incurring current leakage from neighboring ...
Get Vertical 3D Memory Technologies now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

