Chapter 10
General Applicability
So far throughout this book it has been relatively easy to categorize the uses of BGP into chapter-length chunks. There are, however, a number of applications for BGP that I haven't discussed yet. This chapter contains information on those applications, together with some small sections containing information on other general topics on using BGP in SR-OS that frequently generate “How do I…” or “Why does the system do…” questions.
IPv6 PE Router (6PE)
6PE provides the ability to interconnect IPv6 islands over an IPv4 MPLS backbone using IPv6-enabled PE routers and is described in RFC 4798.
The PE routers operate as dual-stack with native IPv6 toward the IPv6 CE and IPv4 toward the core. IPv6 routes are exchanged between the PE and CE using an IGP or BGP, and advertised between PE routers using Multi-Protocol BGP AFI 2 (IPv6) SAFI 4 (NLRI with MPLS labels) to indicate the presence of a label. In SR-OS this label is always the Explicit-Null label (value 2). Like its IPv4 counterpart, the NLRI of the MP_REACH_NLRI attribute is encoded as a triple in the form <length, label, prefix>. Note that, unlike the extensions to BGP/MPLS IP-VPN for IPv6 described in Chapter 3 (referred to as 6VPE), 6PE does not provide any VRF-awareness.
Figure 10-1 MP_REACH_NLRI Labeled BGP Encoding
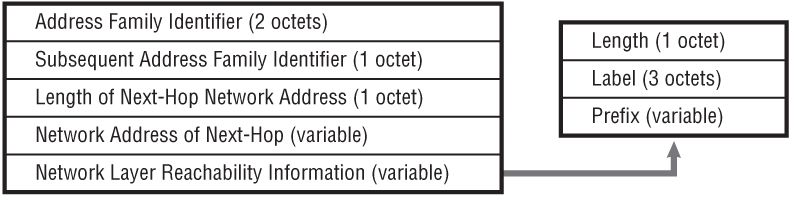
In the data plane, an IPv4 MPLS LSP must exist between ingress PE and egress ...
Get Versatile Routing and Services with BGP: Understanding and Implementing BGP in SR-OS now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

