Chapter 4. Managing Your Class
Now that we have covered the basics of setting up a course and adding content, we need to take a look at some of Moodle’s underlying capabilities. At first glance, this may seem like administrivia, but understanding roles and groups is one of the keys to unlocking Moodle’s full potential as a learning environment. A person’s role in a course determines what he can do—in other words, what capabilities he has. It’s a very powerful system, but it does have a bit of underlying complexity. You can use groups to create student workgroups, recitation sections, or any other arbitrary grouping you need to realize your learning design.
We will start by discussing roles, since anyone who wants to do something in your course needs to be assigned a role.
Understanding and Using Roles
This section covers the following MTC skills: 7.1 Enrolling participants; 7.5 Roles
The new roles and permissions system in Moodle provides you with a huge amount of flexibility for managing how students and other people interact with your course. In older versions of Moodle (prior to 1.7), there were only six roles possible: guest, student, non-editing teacher, editing teacher, course creator, and administrator. Whilst the new system supports these roles out of the box, it also allows you to create and customize roles, and to change what a given role can do in each activity. For example, you can now create permissions in individual forums, which allows you to let students act as moderators in one forum while you retain the moderator role in all of the other forums in your course.
If it seems a bit daunting, don’t worry. Using roles and permissions is something you can take slowly. You can start the usual way, assigning people as students, teachers, and other roles specified by your institution. Later, when your course design grows more elaborate, you can begin to experiment with overrides and assigning specific roles in specific contexts.
We’ll start simply, by assigning users to predefined roles in your course. Then we’ll take a look at the roles and capabilities system and later discuss how to use the advanced features.
Assigning Roles in Your Course
Most of the time, students will enroll themselves or be added automatically by your university’s enrollment system, so there shouldn’t be much need for you to manually enroll students. However, if you need to add a teaching assistant, an outside guest, or a student who is having a problem with financial aid, you must manually enroll them, i.e., assign them a role in your Moodle course.
Warning
By default, teachers are only allowed to assign the roles of non-editing teacher, student, and guest. If you want to assign the role of teacher, you will need to ask your system administrator for this to be allowed.
To assign a user the role of student:
Choose the type of role you wish to assign, e.g., student
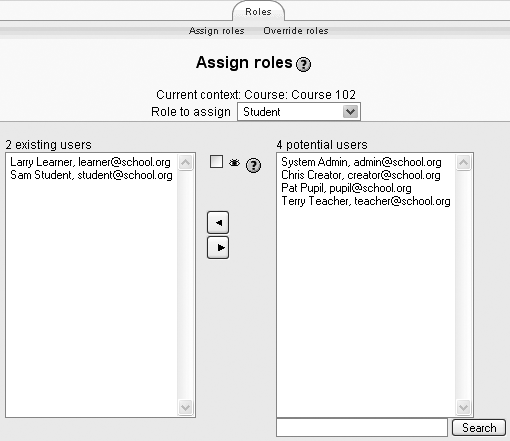
On the “Assign roles” page, there are two columns, as shown in Figure 4-1. The left column lists users who currently have that role, and the right column lists users who don’t.
Warning
Users must have an account on your Moodle site before you can assign them a role in your course. If they don’t appear in either the existing or potential users list, they will need to create an account before they can be assigned a role.
Between the two columns is a hidden assignment checkbox next to an eye icon, for hiding which role a user is assigned to so that the user doesn’t appear in the list of course participants. Click the checkbox before assigning a role if required.
Note
Role assignments are not hidden from admins or teachers. They can always see who is assigned a role in a course.
Tip
Hidden assignments are also useful if you don’t want everyone with teacher rights to be listed in the course description on the front page of your Moodle site.
Find the student you want to add to your course in the righthand column. You can limit the list by searching for the student’s name or email in the Search box below the righthand column.
Select the student’s name from the list and use the left-facing arrow button to add the student to the list in the lefthand column.
Tip
You can add multiple students by holding down the Shift key to select a number of students in a row. If you want to select multiple students who aren’t listed next to each other, hold down the Ctrl key (or Apple key on a Mac) and click each name you want to add.
Students will have access to your course as soon as you assign them a role. They won’t need to have an enrollment key or to confirm the enrollment.
Removing Students
If a student drops your class, you’ll want to remove the student from your Moodle course as well. Leaving a student enrolled in your Moodle course when she is not on the official roster makes grading and class management much more difficult. When you record grades or look for student assignments, extra students on the roll gets confusing. The nonparticipating student will also have access to your discussion boards and other potentially sensitive information.
Fortunately, removing students is easy. Simply reverse the above procedure.
Managing Enrollment
If your university doesn’t have an automatic enrollment system, then ensuring that only students who are officially enrolled in your course have access to your Moodle course can be tricky.
Jason: At my university, students used to be able to drop and add courses at will for the first three weeks of the semester. Many instructors found it difficult to track the constant movement in the roster.
To minimize the amount of work you need to invest in this administrative detail, we recommend a three-pronged strategy.
First, use the course enrollment settings to limit who can enroll in the course and when. Set an enrollment period for the length of your drop/add time. Be sure to set an enrollment key as well. Only students who know the key will be able to enroll in your course, so you won’t need to worry about students enrolling without permission. For more information on these settings, see Chapter 2.
Second, closely monitor your official course roster during the drop/add period. Be consistent about dropping and adding students on a regular basis so you don’t have a big mess at the end of registration.
Third, encourage students who are enrolled to create an account and join your Moodle course as quickly as possible. Many instructors make logging in and joining their Moodle course a small, mandatory assignment. This helps students by forcing them to access your online resources early in the semester, and it makes enrollment management easier for you, since you won’t have to add as many students manually.
Capabilities and Permissions
The new roles system introduces some new terminology that is important to understand before you dive in.
Note
This may be confusing at first, but it’s worth taking some time to understand the power of the new system.
Jason: I was part of the design team for this system and even I had to look up a few details!
There are four primary concepts to understand:
- Role
A role is an identifier of the user’s status in some context (e.g., teacher, student, forum moderator).
- Capability
A capability is a description of a particular Moodle feature (e.g., moodle/blog:create). Capabilities are associated with roles. There are over 150 capabilities within Moodle.
- Permission
A permission is a value that is assigned to a capability for a particular role.
- Context
A context is the scope within which a role assignment is valid. Contexts are organized in a hierarchy, where lower (more specific) contexts inherit capabilities from higher (less specific) contexts. The contexts in Moodle in order of inheritance are:
- System
All contexts in the site, including site settings and user administration
- Site
- Course category
- Course
A single Moodle course
- Module
A module instance within a course (a specific forum, quiz, wiki, etc.)
- Block
A specific block instance within a course (at the time of this writing this feature is not fully implemented)
- User
Roles are made up of a matrix of capabilities and permissions that determine what a user can do within a given context. For example, a user may have course creator privileges at the site level but be unable to post to a particular forum in a certain course.
The permissions determine whether someone can use a capability. Permissions may be set to one of four values:
- Inherit
The default setting. If a capability is set to inherit, the user’s permissions remain the same as they are in a less specific context, or another role where the capability is defined. For example, if a student is allowed to attempt quiz questions at the course level, his role in a specific quiz will inherit this setting.
- Allow
This enables a user to use a capability in a given context. This permission applies for the context that the role gets assigned plus all lower contexts. For example, if a user is assigned the role of student in a course, she will be able to start new discussions in all forums in that course (unless a forum contains an override with a prevent or prohibit value for the capability).
- Prevent
Prevent disables a capability for a user in a given context but does not disallow it in a more specific context. You can prevent students from adding attachments to forum posts in your course, but allow them to do so in one particular forum.
- Prohibit
Prohibit is rarely needed, but occasionally you might want to completely deny permissions to a role in a way that cannot be overridden in any lower context.
Keep in mind that permissions are set within a role, and then people are assigned to roles in a given context. A person can be assigned to more than one role, depending on the context, or even multiple roles within the same context.
Role Overrides
The capabilities within a given role can also be overridden within a specific context. Let’s say you want to create a forum in which students can rate each other’s forum posts. (By default, only teachers can rate forum posts.)
The way to achieve this is through a role override. As long as the capabilities you want to allow your students to have in your course (or within a module in your course) aren’t prohibited at a higher level, you can override the permissions. Within your course, for example, you can override roles at the course level or in a particular activity. If you want to change what students can do anywhere in your course, override the role at the course level. If you want to create a different set of permissions for a given activity, override the role in the activity itself.
Warning
Overriding roles is itself a permission. By default, teachers are unable to override roles so this ability must first be granted by your system administrator for the course or site as appropriate. They must also set which roles can be overridden by the teacher role. If you don’t see the “Override roles” link in the Roles tab, ask your system administrator.
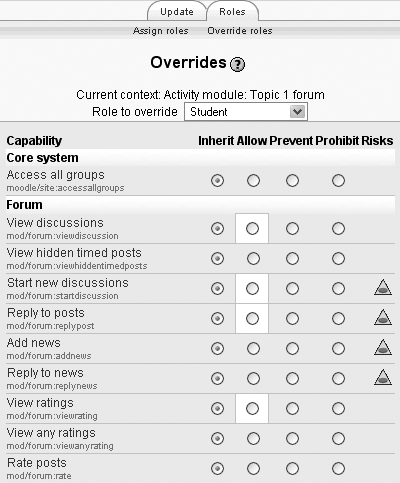
The override interface will only show you the capabilities for the context you are overriding. So if you want to allow students to rate forum posts, you can override the student role in a particular forum. You will only see the forum capabilities in the interface, as shown in Figure 4-2.
To set a role override for an activity:
Click the Update button for the activity for which you want to create the override.
Click the Roles tab and then click the “Override roles” link just below the tabs.
Choose the role you want to override, e.g., student.
Modify the permissions for the override on this activity. (The permissions the role currently has are highlighted in white.)
Warning
Be sure to read the security risks (indicated by the yellow triangle on the right side of the permissions list) for each capability. Some capabilities can present severe risks to student data if you are not careful.
Click the “Save changes” button. Anyone with the role you have just overridden will now have those capabilities in this activity when they next log in to Moodle.
To set a role override at course level:
Click “Assign roles” in the Administration block.
Click the “Override roles” link.
The remaining steps are the same as for setting a role override for an activity.
Overrides allow you to create a lot of variation in the way students interact with an activity. However, before digging into the overrides system itself, be sure you have a clear understanding of what you are trying to achieve educationally with the override.
Assigning Roles in Activities
In addition to assigning roles in your course, you can also assign roles in activities. Let’s say you want to create a forum and allow particular students to moderate the discussions. To moderate, they will need to be able to delete posts, edit posts, and move threads. But the normal student role doesn’t allow them to do these things, nor do you want them to be able to moderate other forums in your course, or all students to be able to moderate.
The way to achieve this is by assigning a role in the activity module context. If you assign the role of non-editing teacher to the students you want to moderate forum discussions, then the students will have non-editing teacher capabilities in that forum only.
The method of assigning a role in the activity module context is very similar to assigning a role in your course.
To assign a user a role in an activity module context:
Click the Update button for the activity in which you want to assign a role.
Click the Roles tab.
Choose the role you want to assign, e.g., non-editing teacher.
On the “Assign roles” page, find the user you want to assign the role to in the righthand column.
Select the user’s name from the list and use the left-facing arrow button to add the user to the list in the lefthand column. The user will now have the role you have just assigned in the activity when he next logs in to Moodle.
Note
Depending on the capabilities you want to allow, there may not be a suitable role you can assign. You may need to contact your system administrator and ask for a new role to be created.
Student Groups
This section covers the following MTC skills: 8.1 Using and managing groups
Moodle has an unusual but effective way of managing small student workgroups within your course. You can define groups at the course level, then set each activity to a group mode or leave it available to everyone. The group mode you choose may also determine the behavior of the module. Think of groups as a filter. If you are a member of a group within a course, and an activity is set to group mode, Moodle will filter out any work from anyone who is not part of your group. You are all looking at the same activity, but you can’t interact with anyone who is not in your group.
There are three group mode options:
- No groups
Everyone participates as part of the class. Groups are not used.
- Separate groups
Each group can see only their own work. They can’t see the work of other groups.
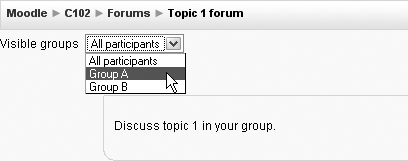
- Visible groups
Each group does their own work, but they can see the work of the other groups as well, as shown in Figure 4-3.
Once the group mode is set for the course or activity, students will interact with your Moodle course as they normally would. The only difference will be the people they meet in certain activities, such as forums. For example, if you set the group mode of a forum to separate groups, Moodle will create a forum for each group. Each student will see the same link to the forum, but she will be able to access only the discussions for her particular group. You need to create the forum only once; Moodle takes care of creating the individual group forums.
To utilize the group mode, you first need to create the student groups:
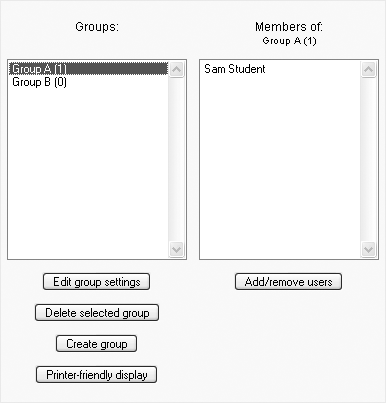
On the Groups page, there are two columns, as shown in Figure 4-4. The left column lists the groups you have created. Initially, this list is empty, as there are no groups created by default. The right column lists the students assigned to the selected group.
To create a new group, click the “Create group” button at the bottom of the page.
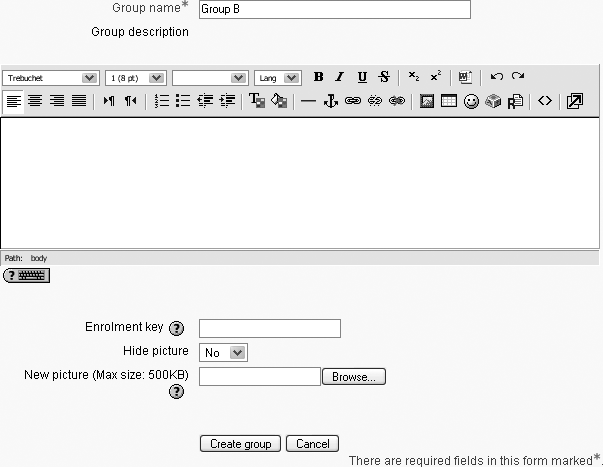
On the “Create groups” page, as shown in Figure 4-5, set the options for your group:
- Group name
This is the name of the group displayed in various places throughout your course.
- Group description
Write a brief description of the group and its purpose. The description is displayed above the list of group members on the Participants page.
- Enrollment key
Enrollment keys allow users to enroll themselves in a course. You can set an enrollment key in your course settings, as we covered in Chapter 2. If you set a group enrollment key too, then anyone who enrolls in the course using that key will also automatically be made a member of the group.
Warning
You need to set an enrollment key in your course settings, as well as set a group enrollment key, otherwise students will not be prompted to enter a key when they attempt to enroll. Students only need to enter the group enrollment key and do not need to know the course settings enrollment key.
Tip
Make sure that the first letter for each group enrollment key is the same as the course settings enrollment key. If a student makes a mistake typing in the enrollment key, he is provided with the first letter of the course settings enrollment key as a hint.
- Hide picture
Hiding the picture for the group prevents the group picture from being displayed in various activities throughout your course.
- New picture
You can upload a profile picture for the group or replace an old picture with a new one.
Click the “Create group” button.
The name of the group will now appear in the groups list. Select the group you just created.
On the “Add/remove users” page, there are two columns, as shown in Figure 4-6. The left column lists the existing members of the group, and the right column lists the potential members. To add a student to the group, select the student’s name from the potential members list and use the left-facing arrow button to add the student to the list in the lefthand column.
Tip
As for assigning users the role of student in your course, you can add multiple students by holding down the Shift key to select a number of students in a row. If you want to select multiple students who aren’t listed next to each other, hold down the Control key (or Apple key on a Mac) and click each name you want to add.
Repeat steps 3 to 7 for each group you need.
Warning
It’s possible to assign students to more than one group. If you do so, it can be confusing for both you and the students. You will need to carefully watch the number of students assigned to each group to make sure you haven’t left someone out. Students will need to be careful about interacting with the right group in the right place. If you have set a module to separate groups mode, students will need to select between the groups where they are members.
Tip
If you have a lot of students to organize into groups, you might like to try the “batch upload of groups” facility. Click “Import” in the Administration block, then follow the instructions in the “upload groups” help file.
If you’ve not forced the group mode in your course settings, you can set it for each activity, either when adding the activity (in the common module settings), or by clicking the group mode icon opposite the activity name when editing is turned on for your course page. The group mode icon toggles between the three possible group modes shown in Table 4-1.
If you’ve forced the group mode in your course settings, then you will not be able to toggle between group modes on your course page.
Backups
This section covers the following MTC skills: 8.6.1 Backup
After spending a lot of time setting up your course and delivering it to your students, you’ll want to make sure you don’t lose your work. Fortunately, Moodle gives you a backup tool to create archives of your courses. Backups can also be used to copy course resources and activities from one course to another.
To make a backup:
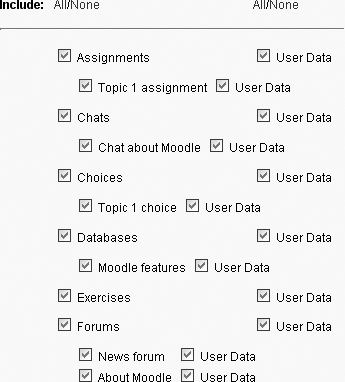
The “Course backup” page, as shown in Figure 4-7, lists all the modules and activities in your course.
Choose which activities you want to include in the backup, and whether to include user data, by using the Include All/None links at the top of the page and/or by selecting the checkboxes next to each module or activity name. User data consists of all student files, submissions, forum postings, glossary entries, etc.
Select the following backup options:
- Meta course
If your course is a meta course, this option will preserve the setting in the restored course.
- Users
This backs up the user accounts for everyone in the course. If you select None, then no user data will be backed up.
- Logs
- User files
This backs up all student submissions for assignments and other file uploads.
- Course files
This backs up any file stored in the files area for the course.
When you have selected your options, click the Continue button to start the backup process.
On the next page, you can preview the files and users that Moodle will include in the backup and, if you wish, change the suggested backup filename, which is backup-COURSESHORTNAME-DATE-TIME.zip.
Tip
If you change your mind about what to include in the backup, you can use your browser’s back button to return to the previous page.
Click the Continue button.
On the next page, the progress of the backup is displayed together with a report if it was successful. You should see the message “Backup completed successfully” at the bottom of the page. Click the Continue button.
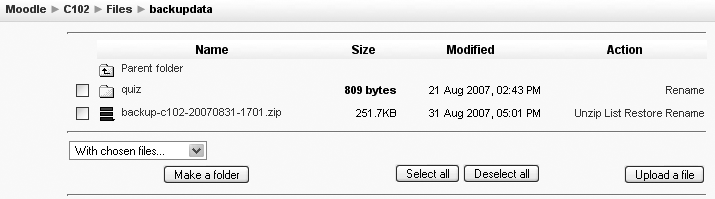
You will then be taken to the backupdata directory in the files area for your course, as shown in Figure 4-8. Click the filename of the backup file to download it to your desktop.
Restoring and Copying Courses
This section covers the following MTC skills: 8.7.1 Restore
Your backup ZIP file can be restored to create a new course or to copy activities into an existing course.
Warning
You will only be allowed to restore to a new course if you have been given appropriate permission at the course category or site level. Contact your system administrator if necessary.
To restore a course:
Either upload a backup ZIP file to your course files area (as covered in Chapter 3) or click Restore in the Administration block to access the backupdata directory, as shown in Figure 4-8.
Click the Restore link opposite the file you want to restore.
On the next page, click Yes to the question “Do you want to continue?” to start the restore process.
Click the Continue button at the bottom of the next page, listing details of the backup.
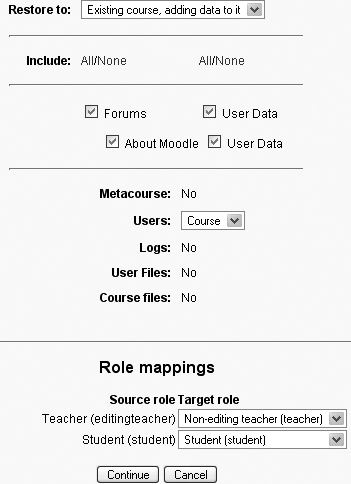
On the next page, as shown in Figure 4-9, select whether you want to restore to the existing course, adding data to it or deleting it first.
If you have permission to restore to a new course, the restore page will contain additional options for setting the new course category, short name, full name, and start date.
Tip
Restoring a course without user data and changing the short name and start date is a good way to roll forward a class you want to use in another semester. An alternative method is to reset the course using the Reset link in your course Administration block.
Choose which activities you want to restore and whether to include user data.
Select course users if you are including user data.
Select appropriate role mappings. The options depend upon the roles you are allowed to assign. By default, teachers are only allowed to assign the roles of non-editing teacher, student, and guest.
Click the Continue button.
On the next page, click the “Restore this course now!” button.
On the next page, the progress of the restore is displayed with a report if it was successful. Click the Continue button.
Reports
This section covers the following MTC skills: 8.3.1 Logs
Once your course is up and students are working, Moodle provides you with detailed logs and participation reports of student activity.
To access course reports:
Click Reports in the Administration block.
On the Reports page, choose from the following:
- Logs
Select any combination of group, student, date, activity, and actions, then click the “Get these logs” button.
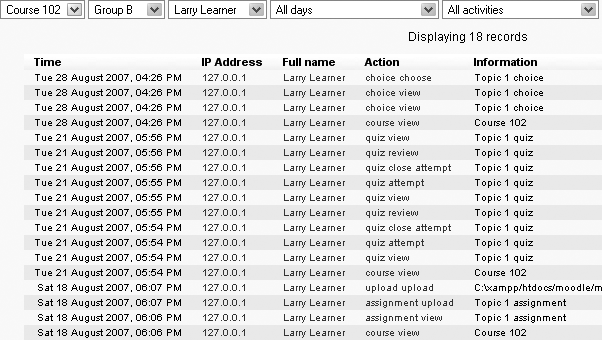
You can see what pages the student accessed, the time and date she accessed it, the IP address she came from, and her actions (view, add, update, delete), as shown in Figure 4-10.
You can choose to display the logs on a page (as shown in Figure 4-10) or download them in text, ODS, or Excel format.
Tip
The Logs page contains active links enabling you to access the student’s profile page or a particular page that the student was viewing. The IP address link provides an estimate of the student’s location.
- Current activity
The “Live logs from the past hour” link in the middle of the Reports page opens a pop-up window listing all course activity in the past hour, which refreshes every minute.
- Activity report
This lists how many times each course activity has been viewed and the last time it was viewed.
- Participation reports
To generate a participation report:
Select an activity module, the time period to look back over, to show only student reports, and the actions you are interested in (views, posts, or all actions), then click the Go button.
A list of all instances of the selected activity module in the course will be generated. Select one, then click the Go button.
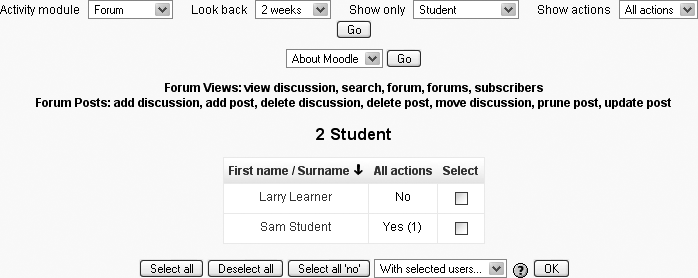
The participation report, as shown in Figure 4-11, lists the number of times each student has done the action selected.
If you wish, you can select particular users and send them a message. Select “Add/send message” from the drop-down menu and click the OK button.
- Statistics
If your system administrator has enabled site statistics, you can also get more detailed summary reports from the statistics menu.
The logs and participation reports are useful for tracking students’ activity in a class. If a student doesn’t spend time with the material, he will have difficulty succeeding in the course. Frequently, students who don’t do well simply haven’t spent the time working with the material.
If you analyze your course reports on a regular basis, you can monitor when your students engage with the course material. You won’t be able to tell exactly how long they spent with a certain activity or resource because the logs report only the time of access. Of course, you can guess how long a student spent with a resource by noting the time when the student began the next activity.
Logs and participation reports can also tell you which resources and activities students find most valuable. For example, if you upload all your PowerPoint slides for students to take notes on in class, but no one accesses them, you might want to find out why.
Get Using Moodle, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.