14.4 Tunnel
A tunnel is an intermediate system that does not need to understand the contents of transferred data. Even encrypted application data can be transferred through a tunnel. It is used by the SSL or TLS protocols. A tunnel is configured in the Secure option in Figure 14.5.
A tunnel is explained in the following figure:
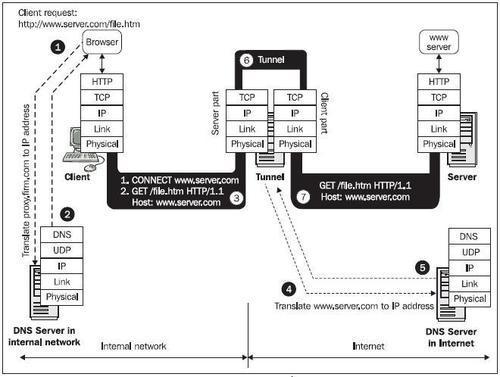
14.7: Tunnel
The client translates a tunnel name into an IP address (1 and 2). The client establishes a TCP connection with the server part of tunnel. Into this created channel, the client usually inserts the CONNECT command with the DNS name and, optionally, the port of the target server (3). The tunnel translates the target ...
Get Understanding TCP/IP now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

