CORRECTIVE 3-3-5 PATTERNS
The A3-B3-C5 patterns consist of normal flats and irregular flats.
Flats
The characteristics of a normal flat are as follows:
- Wave B terminates close to the level of the starting point of Wave A.
- Wave C closes near the level of the terminating point of Wave A.
A flat will generally produce strong subsequent movement. A flat formation (see Figure 4.11 and Figure 4.12) may be composed of repeated flats, totaling counts of 7 or 11 waves. In a five-wave structure, when Wave 2 is a flat, the subsequent Wave 3 can be expected to be as strong as, or stronger than, Wave 1. When Wave 4 is a flat, then Wave 5 will be stronger than Wave 1 and Wave 3. In accordance with the wave principle, flats will often alternate with zigzags.
FIGURE 4.11 Example of a flat formation pattern.
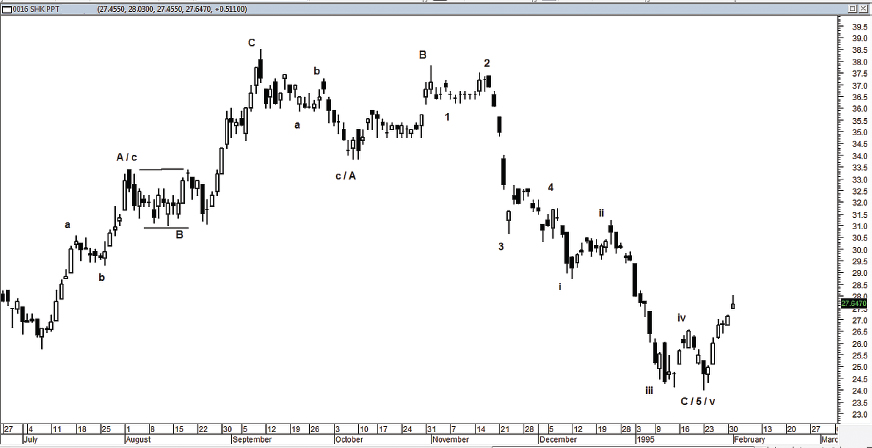
FIGURE 4.12 Formation of a flat pattern in an A-B-C correction.
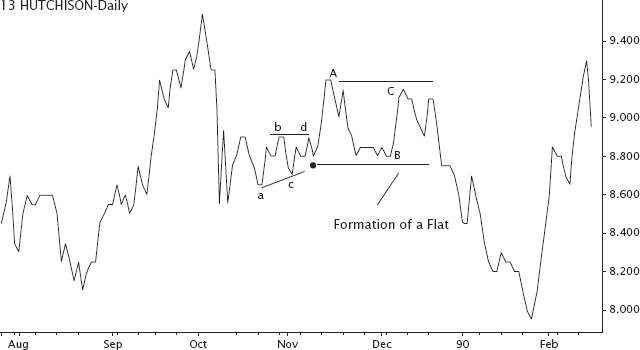
Irregular Flats
In irregular flats (see Figure 4.13 and Figure 4.14), Wave C tends to be the strongest and approximately equals 2.618 of Wave A.
FIGURE 4.13 Formation of an irregular flat with an elongated Wave C.
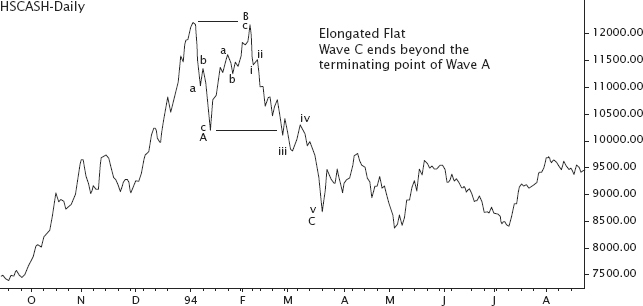
FIGURE 4.14 An irregular flat where Wave B retraces the entire Wave A.
Get Timing Solutions for Swing Traders: A Novel Approach to Successful Trading Using Technical Analysis and Financial Astrology now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

