B.3 Environmental Impacts and Discussion
Environmental impacts are assessed by using the ReCiPe 2008 impact assessment method's (Goedkoop et al., 2009) end points, which are damage to human health, damage to ecosystems, and depletion of resources.
The results in Figure B.3.1 show that the PV-lighting products generally have a lower environmental impact when compared to the other, “conventional” sources of light. The kerosene lamp is the most harmful to the environment on all categories considered. When the kerosene lamp is removed from the assessment, the relative differences between the other lighting systems become more visible. This is shown in Table B.3.1.
Table B.3.1 Life cycle impacts for lighting products, kerosene light excluded.
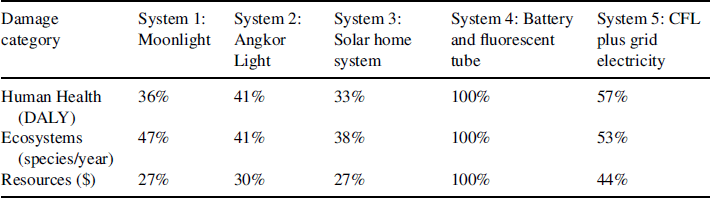
Figure B.3.1 Damage assessment using a ReCiPe impact assessment method, logarithmic scale
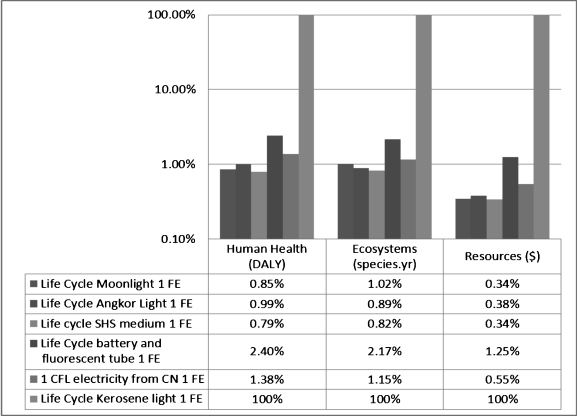
From Table B.3.1, it can be seen that the battery charged with a diesel generator has a larger impact than the other systems considered; however, the impacts from the light plus grid are comparable to those of the “worst” PV-lighting product (although still slightly higher).
It is interesting to see that the drivers of impacts are widely different between the “conventional” lighting solutions and the PV lights. Figure B.3.2 shows that Moonlight's impacts mainly ...
Get The Power of Design: Product Innovation in Sustainable Energy Technologies now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

