21.2. Gates Types and Their Components
Gates are basically part of a winnowing down process. Figure 21.2 shows the NPD funnel which depicts many new product opportunities available to an organization. As these opportunities enter the NPD process and progress through it, the weaker ones (in an absolute or relative sense) are culled by the gatekeepers such that (hopefully) far fewer products are commercialized than were considered or even entered into the NPD process. In a recently completed study, it was found that the percentage of NPD projects drops significantly over the successive stages of development, and NPD projects for radical innovations drop off marginally faster than incremental ones. See Figure 21.3.
NOTE
Gate decisions are the weakest aspect of the NPD process.
Figure 21-2. NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT FUNNEL
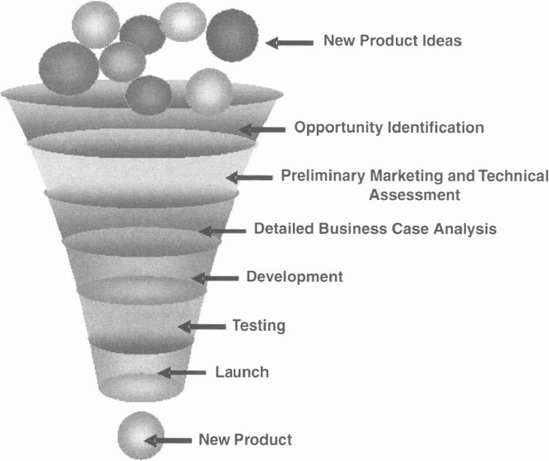
Two types of gates are possible. The first type of gate is called a rigid gate where all necessary criteria must be passed in order to continue the project. Indeed, it is possible in the case of a rigid gate that the failure to reach even a single threshold could derail a NPD project. The second type of gate is called a flexible or permeable gate, which allows a limited number of tasks, frequently those with long lead times, to move forward to the next stage without having to pass all criteria. Cooper (2000) and Rosenau (1996) provide good discussions of rigid and ...
Get The PDMA Handbook of New Product Development now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

