A.1. The RSA algorithm
Two ‘large’ primes p and q are chosen and their product n = pq computed.
An integer e is chosen that is relatively prime to (p − 1)(q − 1)
An integer d is found, for example by using the extension to modular arithmetic of Euclid’s greatest common divisor algorithm, such that:
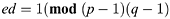
n and e are publicized whilst p, q and d are kept secret.
Encryption of a message m(mod n) can now be performed by anyone knowing the public values n and e by computing:
![]()
If the message does not encode to a number less than n then it must be chopped into ...
Get The Modelling and Analysis of Security Protocols: the CSP Approach now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

