11.11. Routing of PSIs
The concept of a Public Service Identity (PSI; i.e., a URI that is not related to a user but to a service) is explained in Section 3.5.2.
This section is a basic introduction to the routing principles of PSIs, as they are quite different from those that are applied between two IMS users.
As PSIs are not registered, requests to and from them usually do not need to traverse any S-CSCF.
There are three scenarios for PSI routing.
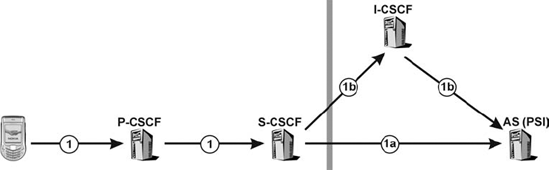
11.11.1. Scenario 1: routing from a user to a PSI
This occurs, for example, when a user calls into a conference (Figure 11.20). In this case the request needs first to traverse the user's S-CSCF, which can then:
Either, resolve the PSI immediately and route it directly to the AS.
Or, is able to resolve the address of an I-CSCF in the home network of the PSI. The I-CSCF will then query the HSS – where routing information about the PSIs will be stored – and route the request directly to the hosting AS. Note that an S-CSCF can also be assigned for the PSI, in which case this would be contacted first. This scenario is not shown here.
Figure 11.20. Routing from a user to a PSI.
11.11.2. Scenario 2: routing from a PSI to a user
This occurs, for example, when a conference server (the focus) invites a user to a conference (Figure 11.21). In this case the AS sends the request:
Either, directly to the I-CSCF of the terminating user's home network, ...
Get The IMS: IP Multimedia Concepts And Services, Second Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

