17.3. Access points
Access points can be understood as IP routers that provide the connection between the UE and the selected service. Examples of such services are:
Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS);
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP);
direct Internet access;
IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS).
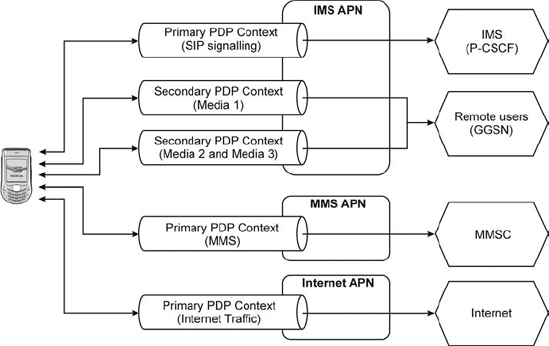
Depending on the operator of the network, more than one of these services might be provided by the same access point. The UE needs to be aware of an Access Point Name (APN) – the address of a GGSN – which gives access to the service-providing entity (e.g., an MMSC, the Internet or the P-CSCF). One GGSN may provide different services that can be accessed by different APNs.
When establishing a primary PDP context with an APN the UE receives an IP address or – in the case of IPv6 – an IPv6 prefix that it has to use when communicating over that PDP context. This means that when a UE has established several connections to different APNs the UE will have different IP addresses for each of the provided services.
Figure 17.1. PDP context types.
Get The IMS: IP Multimedia Concepts And Services, Second Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

