5.5. An Example of Loop Resolution
Rather than deal with all of the concepts in abstract and algorithmic terms, let's take a look at an example of a catenet with loops and see how the STP works to resolve the loops and achieve a tree topology.
|
Before you go off and build a replica of the depicted catenet for use in your organization, be aware that the example is primarily designed to demonstrate STP behavior; as such, it includes a number of interesting boundary conditions and link configurations that rarely occur in most environments. That is, the example is not necessarily practical or useful for any normal purposes. Given that caveat, consider the configuration shown in Figure 5-17.
Figure 5.17. Example configuration
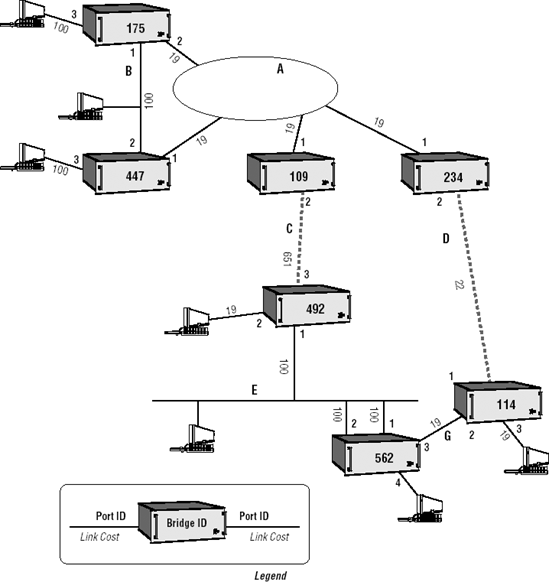
For simplicity, we assume that all of the Bridge and Port Priorities are left at their default values (or set to a common value, which amounts to the same thing). Each bridge is shown with a (simplified) numerical Bridge Identifier, each port with a Port Identifier, and each link with an associated cost.
Following the algorithm described in section ...
Get The All-New Switch Book: The Complete Guide to LAN Switching Technology, Second Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

