As we saw, the FSG cache is distributed randomly between AMPs, which shows that each AMP holds only certain amounts of data. This cache contains as many of the most recently used data rows as will fit in it. When Teradata Database tries to read a database block, it checks the cache first to minimize the I/O and improve the response time of queries. The following figure shows how requests flow for the disk and FAG cache:
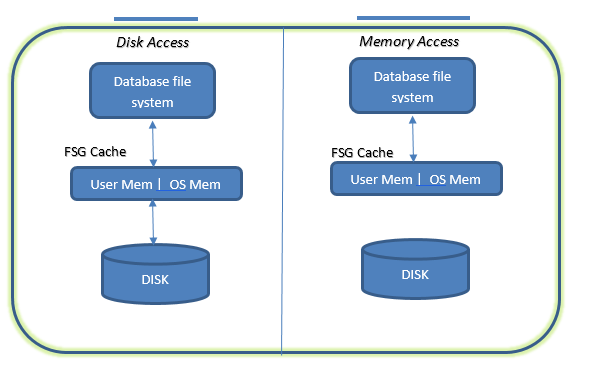
As there are other programs existing on memory, like database programs and OS modules, it is necessary that FSG cache size needs to be optimized. Objects or rows in FSG cache are freed up as per the ageing process. ...

