18.6. CHAPTER 18 REVIEW PROBLEMS
Convert to logarithmic form.
x5.2 = 352 logx352 = 5.2
4.8x = 58 log4.8 58 = x
241.4 = x log24 x = 1.4
Convert to exponential form.
log3 56 = x 3x = 56
logx 5.2 = 124 x124 = 5.2
log2 x = 48.2 248.2 = x
Solve for x.
log81 27 = x 3/4
log3 x = 4 81
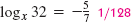
Write as the sum or difference of two or more logarithms.

Express as a single logarithm.
log 5 + log 2 log 10
2 log x − 3 log y log(x2/y3)
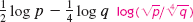
Find the common logarithm of each number to four decimal places.
6.83 0.8344
364 2.5611
0.00638 −2.1952
18.6 1.2695
87.4 1.9415
Find x if log x is equal to the given value.
2.846 701.5
1.884 76.56
−0.473 0.337
3.361 2296
Find the natural logarithm of each number to four decimal places.
84.72 4.4394
2846 7.9537
0.00873 −4.7410
Find the number whose natural logarithm is the given value.
5.273 195.0
1.473 4.362
−4.837 7.931 × 10−3
Find log x if
ln x = 4.837 2.101
ln x = 8.352 3.627
Find ln x if
log x = 5.837 13.44
log x = 7.264 16.73
Solve for x to three significant digits.
(4.88)x = 152 3.17
e2x+1 = 72.4 1.64
3 log x − 3 = 2 log x2 1.00 × 10−3
log(3x − 6) = 3 335
A sum of $1500 is deposited at a compound interest rate of compounded quarterly. How much to the nearest dollar will it accumulate to in ...
Get Technical Mathematics, Sixth Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

