When you choose File→Save, you’re asked where you want the new document stored on your hard drive, what you want to call it, and what Finder tags (Broken Aliases) you want applied to it. The resulting dialog box is a miniature Finder. All the skills you’ve picked up working at the desktop come into play here.
To give it a try, launch any program that has a Save or Export command—TextEdit, for example. Type a couple of words, and then choose File→Save. The Save sheet appears (Figure 4-25).
Tip
In most programs, a quick glance at the Close button in the upper-left corner of a window tells you whether it’s been saved. When a small dot appears in the red button, it means you’ve made changes to the document that you haven’t saved yet. (Time to press ⌘-S!) The dot disappears as soon as you save your work.
In programs that offer the Auto Save and Versions features described later in this chapter, like TextEdit, the red-dot convention has been retired. Instead, when you’ve made changes to a document since saving it, you see the light-gray word Edited in the title bar.
When you save in most Mac programs, a little Save dialog box called a sheet slides directly out of the document’s title bar. This little Save box is a sticky note attached to the document . It stays there, neatly attached and waiting, even if you switch to another program, another document, the desktop, or wherever. When you finally return to the document, the Save sheet is still there, waiting for you to type a file name and save the document.
Of course you have probably never saved a document into some deeply nested folder by accident, never to see it again. But millions of novices (and even a few experts) have fallen into this trap.
When the Save sheet appears, a pop-up menu shows you precisely where the Mac proposes to put your newly created document: usually in the Documents folder of your own Home folder. For many people, this is an excellent suggestion. If you keep everything in your Documents folder, it will be extremely easy to find, and you’ll be able to back up your work just by dragging that single folder to a backup disk.
As shown at top in Figure 4-25, the Where pop-up menu gives you direct access to some other places where you might want to save a file. (The keystrokes for the most important folders work here, too—Shift-⌘-H for your Home folder, for example.)
In any case, when you save a file, the options in the Where pop-up menu have you covered 90 percent of the time. Most people work with a limited set of folders for active documents.
But when you want to save a new document into a new folder, or when you want to navigate to a folder that isn’t listed in the Where pop-up menu, click the ![]() button identified in Figure 4-25. The Save sheet expands into a miniature version of the Finder.
button identified in Figure 4-25. The Save sheet expands into a miniature version of the Finder.
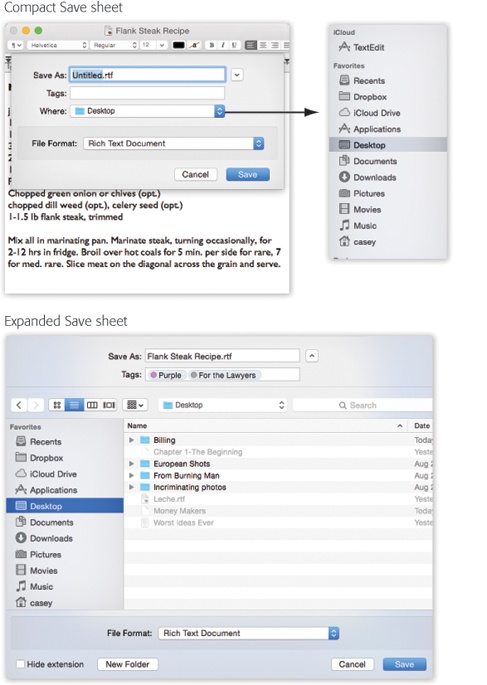
Figure 4-25. Top: The Save dialog box, or sheet, often appears in its compact form. Right: If you open the Where pop-up menu, you’ll find that OS X lists all the places it thinks you might want to save your new document: online (iCloud), on the hard drive, in a folder you’ve put into your Sidebar (“Favorites”), or into a folder you’ve recently opened. Bottom: If you want to choose a different folder or to create a new folder, click the ![]() button (next to the Save As box) to expand the dialog box. Here you see the equivalent of the Finder—with a choice of icon, list, or column view. Even the Sidebar is here, complete with access to other disks on the network. Tip: In most programs, you can enlarge the Save or Open dialog box by dragging one of its edges. You can also adjust the width of the Sidebar by dragging its right edge.
button (next to the Save As box) to expand the dialog box. Here you see the equivalent of the Finder—with a choice of icon, list, or column view. Even the Sidebar is here, complete with access to other disks on the network. Tip: In most programs, you can enlarge the Save or Open dialog box by dragging one of its edges. You can also adjust the width of the Sidebar by dragging its right edge.
Tip
You can switch back and forth between the compact and expanded versions of this dialog box by pressing the undocumented shortcut ⌘-=.
You might be shocked to find out just how many Finder features are available, all within this little Save dialog box. For example:
Navigate with the Sidebar. It’s here, complete with access to the other computers on your network, and your iCloud Drive.
Navigate with keystrokes. All the usual keyboard shortcuts for navigating your Mac work within the Open and Save boxes. You can press ⌘-D to see what’s on your desktop, Shift-⌘-H for your Home folder, Shift-⌘-A for your Applications folder, and so on.
Switch views with the toolbar buttons, like
 /
/ and icon, list, column, and even Cover Flow views.
and icon, list, column, and even Cover Flow views.Tip
In column view, your first instinct should be to widen this window, making more columns available. Do so by carefully dragging either edge of the dialog box. The Mac remembers the size for this Save sheet independently in each program.
And in list view, how’s this for a tip? If you right-click (or two-finger click) one of the column headings, like Name or Date Modified, you get a secret pop-up menu of column names: Last Opened, Size, Kind, Label, and so on. That’s right: You can customize the list view within an Open or Save dialog box. You can sort, too, by clicking one of the column headings, just as at the desktop.
Search for files. The search box at the top of the Open or Save dialog box is a clone of the Finder’s search box (Chapter 3). Press ⌘-F to make your insertion point jump there. Type a few letters of the name of the file or folder you’re looking for, and up it pops, regardless of its actual hard-disk location.
Delete a document or folder right from this list. Either right-click it and choose Move to Trash, or select it and press ⌘-Delete (the same “delete this” keystroke you use in the Finder).
Rename a document or folder. Right-click (or two-finger click) it; from the shortcut menu, choose Rename. (That’s new in El Capitan.)
Create a new folder. Click New Folder (or press the usual New Folder keystroke, Shift-⌘-N) to create a new folder inside the folder you’re looking at.
You’re asked to type the new name for the folder. After you’ve done so, click Create (or press Return). The new folder appears and opens before you, empty. You can now proceed with saving your new document into it, if you like.
Use Quick Look (Quick Look). Select a file or folder in the list and tap the space bar to view it in a full-size window.
Add folders to the left-side Favorites list. Drag them into the Sidebar here, either from the desktop, if it’s visible, or right out of the dialog box in front of you. You can remove things from the Sidebar, too; just drag them away.
Navigate from the keyboard. Most of the familiar Finder navigation shortcuts work here, too. Press the
 and
and  keys to navigate the columns, or the
keys to navigate the columns, or the  and
and  keys to highlight the disk and folder names within a column. Once you’ve highlighted a column, you can also type to select the first letters of disk or folder names.
keys to highlight the disk and folder names within a column. Once you’ve highlighted a column, you can also type to select the first letters of disk or folder names.Get Info. Even in the Save or Open dialog box, you can highlight an icon (or several) and then press ⌘-I. You switch back to the Finder, where the Get Info box is waiting with the date, size, and other details about the selected icons.
When you’re finished playing around, open the folder where you want to save your newly created document and then click Save to store it there.
Tip
Here’s one of the weirdest tricks yet. When the Open or Save dialog box is open before you, you can press Shift-⌘-period to make all your Mac’s hidden files appear. (As a Unix-based outfit, OS X is crawling with these invisible files.) Press that keystroke again to re-hide the hidden files. Fun for geeks! If you use a non-American number-formatting system (where one thousand is 1.000, for example), then use Shift-⌘-comma instead.
The next time you save a new document, the Save sheet reappears in whatever condition you left it. That is, if you used column view the last time, it’s still in column view. At any time, you can collapse it into simplified view, shown at top in Figure 4-25, by clicking the ![]() button to the right of the Save As pop-up menu.
button to the right of the Save As pop-up menu.
Tip
For years, there’s been a keyboard shortcut for the Don’t Save button that appears when you close a new document without saving it: ⌘-D. But in many modern Apple programs, including TextEdit, Preview, Grab, Pages, and Keynote, the button says Delete instead of Don’t Save. In those cases, press ⌘-Delete to “click” it instead of using the mouse.
Whether you’re using the mini-sheet or the expanded view, you can save yourself some folder-burrowing time by following this very weird tip: You can specify a folder location by dragging the icon of any folder or disk from your desktop directly into the Save or Open sheet. OS X instantly displays the contents of that folder or disk. This feature is totally undocumented—but well worth learning.
Tip
If, when the Save box is in its expanded condition, you click the name of an existing file, OS X thoughtfully copies the name of the clicked file into the Save As text box (which otherwise said “Untitled” or was blank).
This trick can save you time when you’re saving a second document with a slightly modified name (“Oprah and Me: The Inside Story, Chapter 1” and then “Oprah and Me: The Inside Story, Chapter 2”). It’s also useful if you want to replace the original file with the new one you’re saving. Instead of having to type out the entire name of the file, you can just click it.
The Save dialog box in many programs offers a pop-up menu of file formats below the Save As box. Use this menu when preparing a document for use by somebody else—somebody whose computer doesn’t have the same software. For example, if you’ve used a graphics program to prepare a photograph for use on the web, this menu is where you specify JPEG format (the standard web format for photos).
The dialog box that appears when you choose File→Open is almost identical to the expanded Save File sheet. Because you encounter it only when you’re opening an existing file, this dialog box lacks a Save button, a Tags box, a file name field, and so on.
Note
Furthermore, the Open dialog box gives you access only to disks, folders, and documents that you can actually open at this moment. For example, when you’re using GarageBand, picture files show up dimmed.
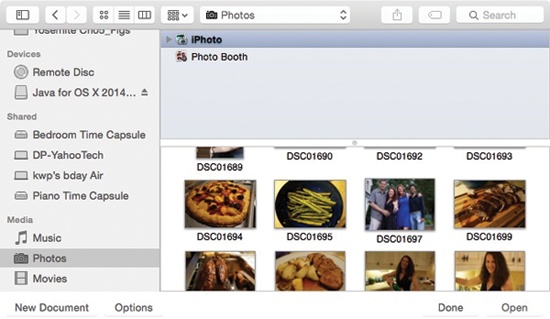
But the Open box adds a special Sidebar category called Media (see Figure 4-26), which gives you direct access to all your photos, music, and movies. Apple figures you might want to import these items into a document you’re working on.
Figure 4-26. The Media Browser is built right into the Open box. You get miniature listings of your iTunes, Photos, and movie files right in the Sidebar, for convenience in importing them into (for example) Keynote, PowerPoint, or a web design program.
Most of the other Save File dialog box controls are equally useful here. That handy Spotlight search bar is still there, only a ⌘-F away. Once again, you can begin your navigation by seeing what’s on the desktop (press ⌘-D) or in your Home folder (Shift-⌘-H).
Once again, you can find a folder or a disk by beginning your quest with the Sidebar and then navigate using icon, list, or column view. And, once again, you can drag a folder, disk, or file icon off your desktop directly into the dialog box to specify where you want to look. (If you drag a file icon, you’re shown the folder that contains it.)
When you’ve finally located the file you want to open, double-click it or highlight it (which you can do from the keyboard), and then press Return or ⌘-O.
In general, most people don’t encounter the Open File dialog box nearly as often as the Save File dialog box. That’s because the Mac offers many more convenient ways to open a file—double-clicking its icon in the Finder, choosing its name from ![]() →Recent Items, and so on—but only a single way to save a new file.
→Recent Items, and so on—but only a single way to save a new file.
Get Switching to the Mac: The Missing Manual, El Capitan Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.