10.2 Errors in Testing
It should be intuitively clear that since sample information is used to test hypotheses about a population parameter, an element of uncertainty is involved in assessing the test results. Hence it is possible to reach a “false conclusion.” The two types of errors encountered are:
In fact, the complete set of possible actions given the status of the null hypothesis are presented in Table 10.1.
Table 10.1 Types of Errors.
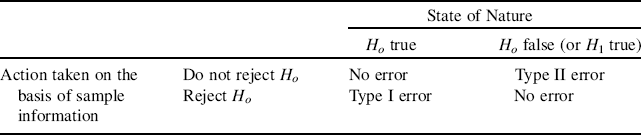
The risks associated with wrong decisions are the (conditional) probabilities of committing Type I and Type II Errors:
Get Statistical Inference: A Short Course now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

