Appendix 8.A A Confidence Interval for the Population Median MED
When a population distribution is highly skewed or has heavy tails, the median is a better measure of central location than the mean. Moreover, we noted at the end of Section 8.4 that using the t statistic when sampling from such populations is not appropriate and can lead to misleading interval estimates of μ, especially for small samples. Given that the sample median med serves as an estimator for the population median Med, let us construct a 100(1 − α)% confidence interval for Med that is centered on med. Before doing so, however, we need to examine the notion of an order statistic. This concept will enable us to develop a convenient notational device for specifying a confidence interval for the population median.
Specifically, the order statistics associated with the random sample ![]() are the sample values arranged in an increasing sequence and denoted as follows:
are the sample values arranged in an increasing sequence and denoted as follows:
(8.A.1) ![]()
where, for 1 ≤ i ≤ n,
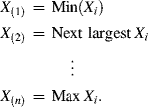
For instance, given the seven sample observations on X: 6, 2, 4, 8, 19, 3, 10, the set of order statistics are as follows:
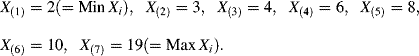
Stated ...
Get Statistical Inference: A Short Course now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

