Storing the data column by column instead of row by row gives you the opportunity to store each column in a sorted way. Imagine that you have every column totally sorted. Then for every equijoin, the merge join algorithm could be used, which is, as you already know, a very efficient algorithm. In addition, with sorted data, you get one more type of compression for free—run-length encoding (RLE) compression.
The following figure explains the idea graphically:
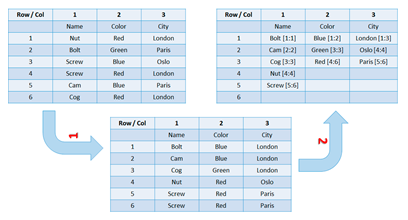
An RDBMS in the first step reorders every single column. Then RLE compression is implemented. For example, if you look ...

