17.2. Wait analysis
Prior to SQL Server 2005, the only means of obtaining information on wait statistics was through the use of the undocumented DBCC SQLPERF(waitstat) command. Fortunately, SQL Server 2005 (and 2008) provides a number of fully documented DMVs for this purpose, making them a central component of wait analysis.
Figure 17.2. SQLOS uses one scheduler per CPU core. Each scheduler processes SPIDs, which move among the running, suspended, and runnable states/queues.
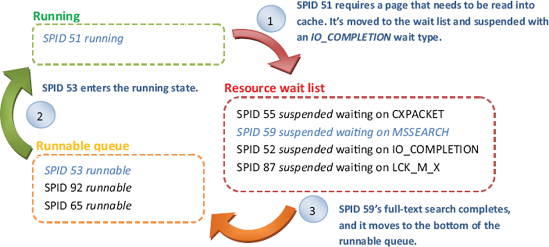
Let's look at wait analysis from two perspectives: at a server level using the sys.dm_os_wait_stats DMV and at an individual process level using extended events. This ...
Get SQL Server 2008 Administration in Action now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

