6.4 MPEG Surround decoder
6.4.1 Structure
The MPEG Surround decoder structure is outlined in Figure 6.8. The down-mix is first processed by a pre-gain, which is the inverse of the post-gain of the MPEG Surround encoder. Subsequently, the input signals are processed by an analysis filterbank that is identical to the filterbank described in Section 6.3.3. A spatial decoder regenerates multichannel audio by reinstating the spatial properties described by the decoded parameters. Finally, applying a set of synthesis filterbanks and post-gains (the inverse of the encoder pre-gains) results in the time domain multi-channel output signals.
6.4.2 Spatial decoder
Operation principle
The spatial decoder generates multi-channel output signals from the down-mixed input signal by reinstating the spatial cues captured by the spatial parameters. The spatial synthesis of OTT decoding blocks employs so-called decorrelators and matrix operations in a similar fashion as parametric stereo decoders [47]. In a OTT decoding block, two output signals with the correct spatial cues are generated by mixing a mono input signal with the output of a decorrelator that is fed with that mono input signal.
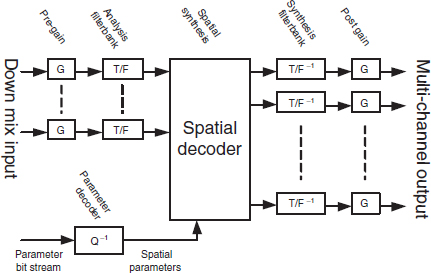
Figure 6.8 Structure of the MPEG Surround decoder. Reproduced by permission of the Audio Engineering Society, Inc, New York, USA.
Figure 6.9 Concatenation of two OTT decoding blocks to achieve three-channel output. ...
Get Spatial Audio Processing: MPEG Surround and Other Applications now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

