Chapter 10
Variable Selection and Model Building
10.1 a. With α = 0.10, the model chosen is y = β0 + β2x2 + β7x7 + β8x8 + ε.
b. With α = 0.10, the model chosen is y = β0 + β2x2 + β7x7 + β8x8 + ε.
c. With αIN = 0.05 and αOUT = 0.10, the model chosen is y = β0 + β2x2 + β7x7 + β8x8 + ε.
d. The three procedures chose the same model.
10.3 The choice of cut-off values is to prevent the circular addition-subtraction of the variables.
10.5 a. The model involves just
x1 with
R2p = 75.3%.
Cp = −1.8 and
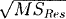
= 3.12.
b. Stepwise leads to the same model involving just x1.
10.7 When FIN = FOUT = 4.0, the model involves only x6. However, when FIN = FOUT = 2.0, the model involves x6 and x7.
10.9 The model involves
x1,
x2,
x3, and
x4 with
R2p = 95.3%,
Cp = 5 and

= .002.
10.11 The model is y = β0 + β1x1 + β2x2 + β4x4 which has a PRESS = 85.35 and R2Pred = 96.86%.
10.13 a. From Section 3.7, we get
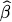
= (
W′W)
−1 W′y0 with
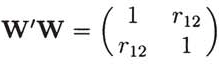
. Therefore,
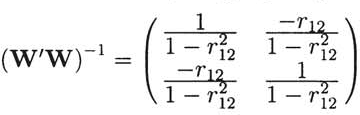
which means that .
b. Since we are fitting a model with only one regressor, the ...
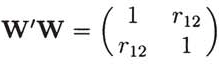 . Therefore,
. Therefore, 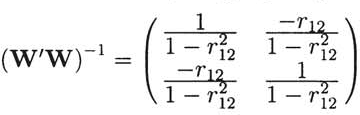 which means that .
which means that .
