 Appendix J
Appendix J
Calculation of the Transmission Coefficient for a Symmetric Resonant-Tunneling Diode
To calculate the transmission coefficient, we consider Fig. 9a of Chapter 8 where the five regions (I, II, III, IV, V) are specified by the coordinates (x1, x2, x3, x4). The Schrödinger equation for an electron in any region can be written as
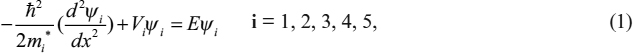
where ![]() is the reduced Planck constant, mi* the effective mass in the ith region, E the incident energy, and Vi and ψi the potential energy and the wave function in the ith region, respectively. The wavefunction ψi can be expressed as
is the reduced Planck constant, mi* the effective mass in the ith region, E the incident energy, and Vi and ψi the potential energy and the wave function in the ith region, respectively. The wavefunction ψi can be expressed as
![]()
where Ai and Bi are constants to be determined from the boundary conditions and ![]() . Since the wavefunctions and their first derivatives (i.e., ψi / mi* =ψi+1 / m*i+1) at each potential discontinuity must be continuous, we obtain the transmission coefficient (for identical effective mass across the five regions)
. Since the wavefunctions and their first derivatives (i.e., ψi / mi* =ψi+1 / m*i+1) at each potential discontinuity must be continuous, we obtain the transmission coefficient (for identical effective mass across the five regions)
![]()
where
H ≡ 2[
Get Semiconductor Devices: Physics and Technology, 3rd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

