3
The Wireless Medium
In this chapter we explain the fundamental concepts related to wireless communications. The material provided is introductory and related to the security issues. For interested readers, further details about the physical layer data communication concepts can be found in Stallings (2000).
3.1 Wireless Channel Fundamentals and Security
Electromagnetic signals can be either analog or digital. The intensity of an analog signal varies and the change in the signal strength is usually smooth and continuous. On the other hand, digital signal strength is constant for a period, after which it may change to another discrete level. Analog and digital signals are depicted in Figure 3.1.
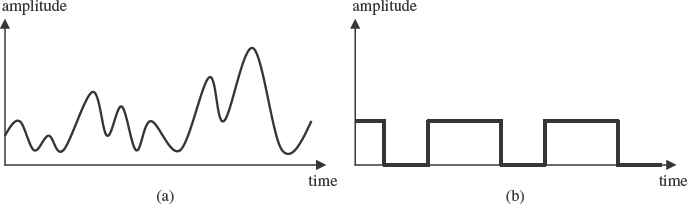
Figure 3.1 (a) Analog and (b) digital signal
When the signal strength is the same as the signal strength a certain time period, T, before, and this repeats every T, the signal is called periodic. Figure 3.2 shows sine and square waves, which are analog and digital periodic signals respectively, where
![]()
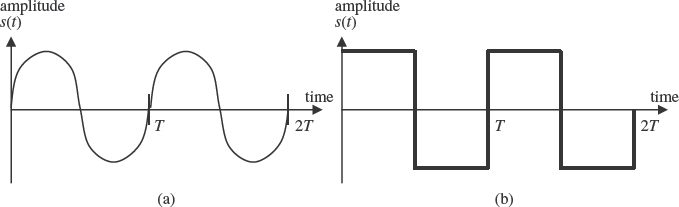
Figure 3.2 (a) Sine and (b) square wave
The frequency (f) of a periodic signal is the rate at which it repeats a complete cycle in every second, i.e. f = 1/T, and this rate is given in Hertz (cycles ...
Get Security in Wireless Ad Hoc and Sensor Networks now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

