Deciding Whether to Use a WHERE Expression or
a Subsetting IF Statement
To conditionally select observations from a SAS data set, you can use either a WHERE
expression or a subsetting IF statement. They both test a condition to determine whether
SAS should process an observation. However, they differ as follows:
• The subsetting IF statement can be used only in a DATA step. A subsetting IF
statement tests the condition after an observation is read into the Program Data
Vector (PDV). If the condition is true, SAS continues processing the current
observation. Otherwise, the observation is discarded, and processing continues with
the next observation.
• You can use a WHERE expression in both a DATA step and SAS procedures, as well
as in a windowing environment, SCL programs, and as a data set option. A WHERE
expression tests the condition before an observation is read into the PDV. If the
condition is true, the observation is read into the PDV and processed. If the condition
is false, the observation is not read into the PDV, and processing continues with the
next observation. This can yield substantial savings when observations contain many
variables or very long character variables (up to 32K bytes). In addition, a WHERE
expression can be optimized with an index, and the WHERE expression enables
more operators, such as LIKE and CONTAINS.
Note: Although it is generally more efficient to use a WHERE expression and avoid
the move to the PDV before processing, if the data set contains observations with
very few variables, the move to the PDV could be cheap. However, one variable
containing 32K bytes of character data is not cheap, even though it is only one
variable.
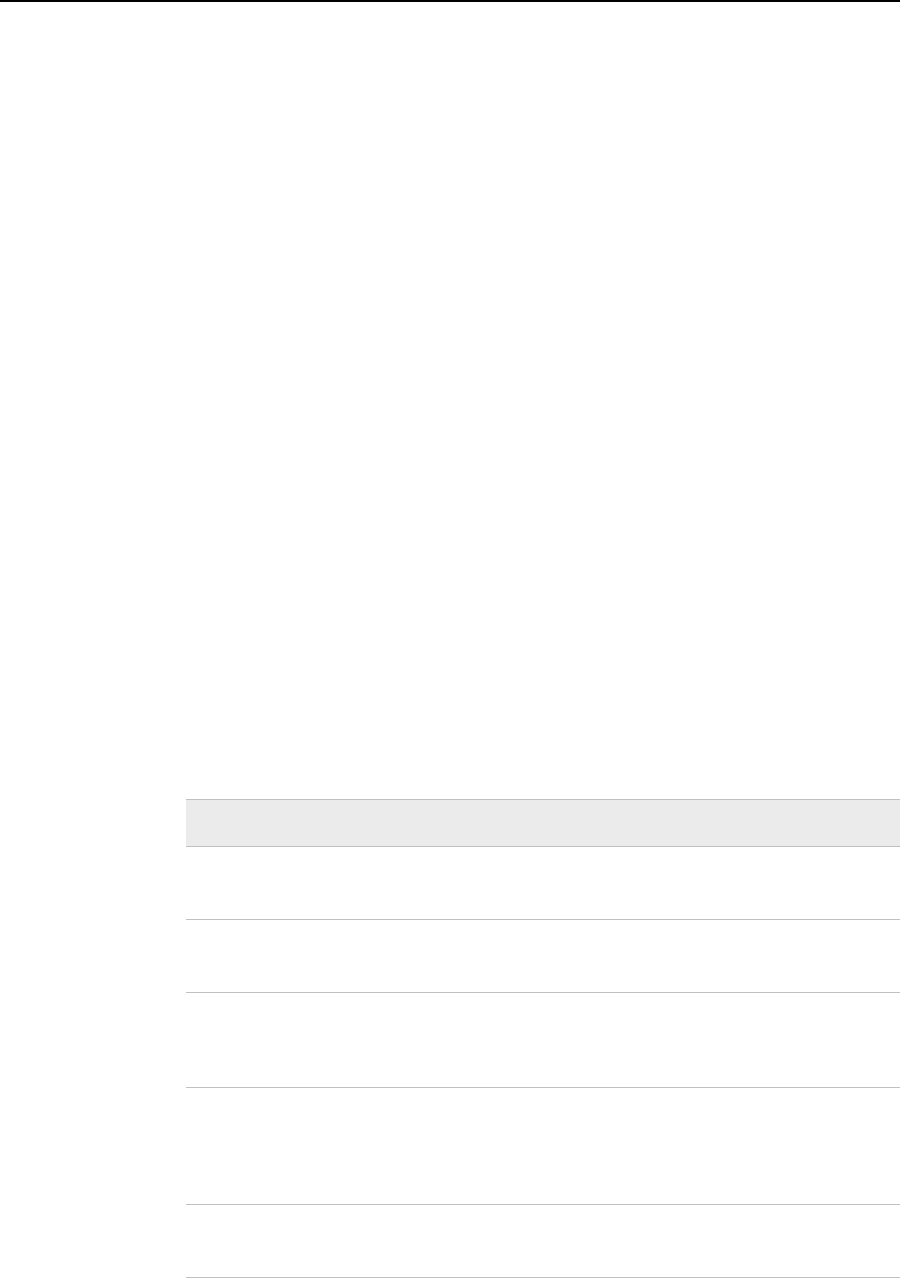
In most cases, you can use either method. However, the following table provides a list of
tasks that require you to use a specific method:
Table 11.6 Tasks Requiring Either WHERE Expression or Subsetting IF Statement
Task Method
Make the selection in a procedure without using a preceding
DATA step
WHERE expression
Take advantage of the efficiency available with an indexed
data set
WHERE expression
Use one of a group of special operators, such as BETWEEN-
AND, CONTAINS, IS MISSING or IS NULL, LIKE, SAME-
AND, and Sounds-Like
WHERE expression
Base the selection on anything other than a variable value that
already exists in a SAS data set. For example, you can select a
value that is read from raw data, or a value that is calculated or
assigned during the course of the DATA step
subsetting IF
Make the selection at some point during a DATA step rather
than at the beginning
subsetting IF
Deciding Whether to Use a WHERE Expression or a Subsetting IF Statement 193
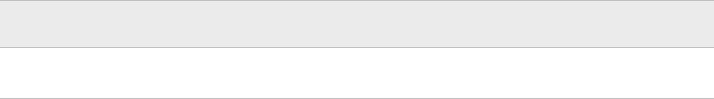
Task Method
Execute the selection conditionally subsetting IF
194 Chapter 11 • WHERE-Expression Processing
Get SAS 9.4 Language Reference, 6th Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

