The window() operator works almost the same, except that, instead of buffering items in a Collection object, it buffers items in another producer.
Here is an example:
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val flowable = Flowable.range(1,111)//(1)
flowable.window(10)
.subscribe {
flo->flo.subscribe {//(2)
print("$it, ")
}
println()
}
}
Let's first see the output, as shown here, before we try to understand it:
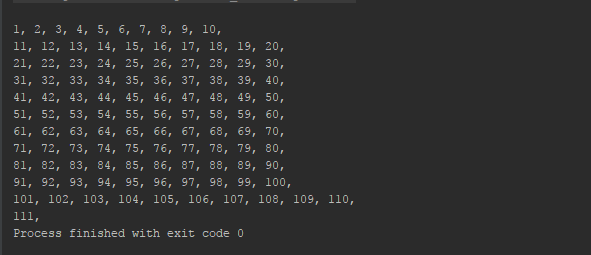
The window operator buffers 10 emissions in a new Flowable instance, which we will again subscribe to inside the flowable.subscribe lambda, and print them with a comma as a suffix.
The window operator also has same functionality ...

