Chapter 8. Parallel Physical Layer Protocol
This chapter describes the physical layer protocol for the RapidIO parallel physical layer. The RapidIO parallel physical layer differs from the serial physical layer in the following ways. The packet and control symbol information is striped across an 8- or 16-bit-wide interface, instead of a single- or four-lane interface (Figure 8.1). The clock information is sent on a separate differential pair and is not encoded in the data stream. The clock signal operates at half the frequency of the data; in other words, the data lines operate at double the rate of the clock signal. There is a separate framing signal that is used to distinguish packets from control symbols. The framing signal serves a purpose very similar to the K-codes in the serial physical layer. Control symbols each have a single function on the parallel interface, on the serial interface control symbols can have up to two separate functions. The parallel interface uses differential electrical signals based on the IEEE LVDS standard, the serial interface uses differential electrical signals based on the IEEE XAUI standard.
Figure 8.1. RapidIO interface differences
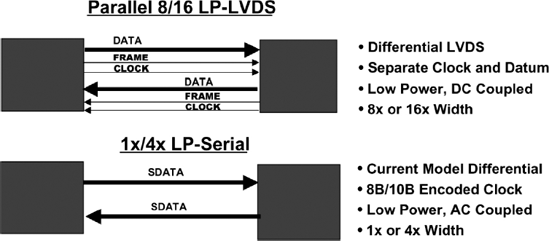
The parallel physical layer is simpler to implement than the serial physical layer. The operating frequencies are significantly lower, with specified clock frequencies ranging from 250 MHz to 1 GHz. The parallel ...
Get RapidIO: The Next Generation Communication Fabric For Embedded Application now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

